Air Compressor Pump:
To compress air,
the piston moves up and down in the
cylinder. On the downstroke, air is drawn
in through the intake valves. The exhaust
valves remain closed. On the upstroke of
the piston, air is compressed. The intake
valves close and compressed air is forced
out through the exhaust valves.
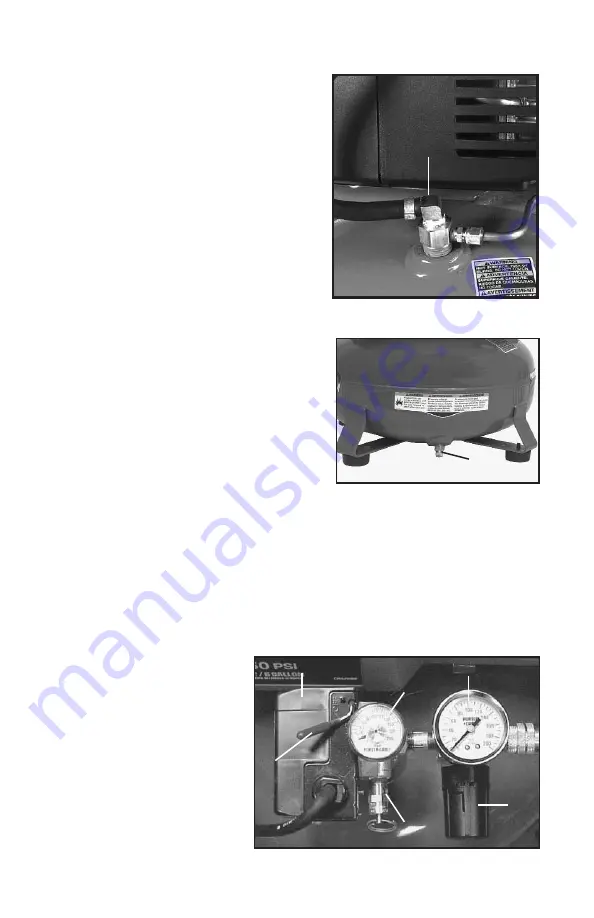
Check Valve (B) Fig. 1:
When the air
compressor is operating, the check valve
is “open”, allowing compressed air to
enter the air tank. When the air
compressor reaches “cut-out” pressure,
the check valve “closes”, allowing air
pressure to remain inside the air tank.
ON/AUTO-OFF Switch (C) Fig. 3:
Turn
this switch ON to provide power to the
automatic pressure switch and OFF to
remove power at the end of each use.
Pressure Switch (D) Fig. 3:
The
pressure switch automatically starts the
motor when the tank pressure drops
below the factory set “cut-in” pressure. It
stops the motor when the air tank
pressure reaches the factory set “cut-
out” pressure.
Regulator (E) Fig. 3:
The air pressure coming from the air tank is controlled by
the regulator. Turn the regulator knob clockwise to increase pressure and
counterclockwise to decrease pressure. To avoid minor readjustment after
making a change in pressure setting, always approach the desired pressure
from a lower pressure. When reducing from a higher to a lower setting, first
reduce to pressure less than that desired, then bring it up to the desired
pressure. Depending on the air requirements of each particular accessory, the
outlet regulated air pressure may have to be adjusted while operating the
accessory.
Outlet Pressure Gauge (F)
Fig. 3:
The outlet pressure
gauge indicates the air
pressure available at the
outlet side of the regulator.
This pressure is controlled
by the regulator and is
always less than or equal to
the tank pressure. See
“Operating Procedures”.
7
E
DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
K
J
F
C
B
G
D






























