- 11 -
11
7. Data Rate:
It shows the statistics of data transfer based on the number of packets transmitted
and received.
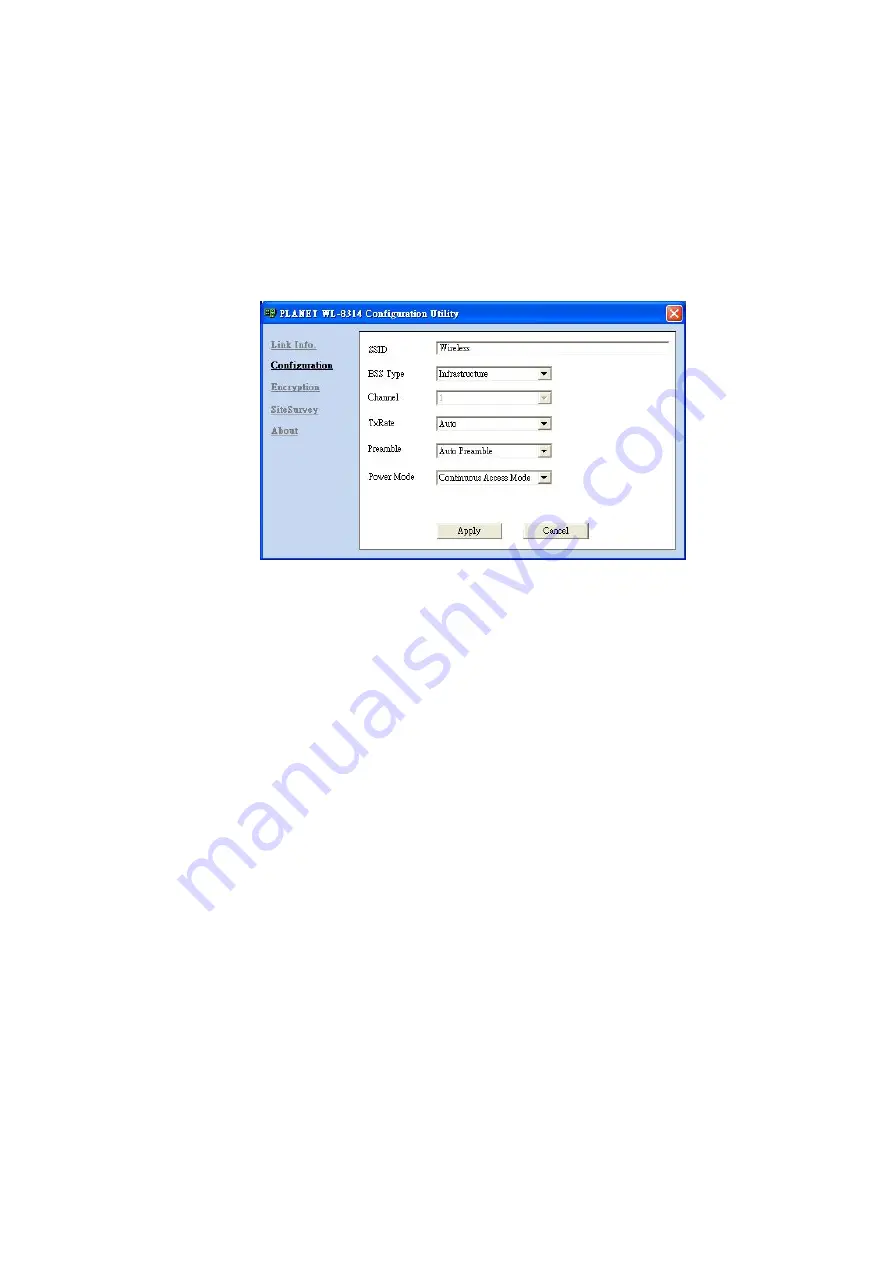
3.2 Configuration
In this page, you can configure the settings of the Access Point you want to connect to or you
have connected to. After making the configuration, please click
“
Apply
”
to make it work or
“
Cancel
”
to give up.
1. SSID:
It must be identical for each wireless clients and devices in the same wireless work.
2. BSS Type:
There are two types available for selection:
(1)Ad-hoc:
This mode allows clients to communicate directly with each other without the use of
an Access Point.
(2)Infrastructure:
This mode requires the presence of an Access Point, via which all
wireless communication is conducted
3. Channel:
It shows the current channel on which the AP is operating. In Infrastructure mode, this
value is fixed, while in Ad-hoc mode it can be changed.
4. Tx Rate:
It shows the data transfer rate. If Auto mode is selected, the device will choose the best
data transfer rate automatically.
5. Preamble (Auto/Long/Short):
There are 3 options: Auto, Short, and Long Preamble.
Preamble is a sequence of bits transmitted at 1Mbps that allows the PHY circuitry to reach
steady-state demodulation and synchronization of bit clock and frame start. It is the first Suffield
of PPDU, which is the appropriate frame format for transmission to PHY (Physical layer). The
Short Preamble minimizes overhead and thus improves throughput performance. However, the
Short Preamble is supported only by IEEE 802.11b (High-Rate) standard and not by IEEE
802.11. That means the stations using Short Preamble cannot communicate with the peers
using Long Preamble. If Auto Preamble is selected, the device will automatically choose the
appropriate preamble type to communicate with the Access Point.
6. Power Mode:
It shows Power Management modes. There are 3 options: Continuous Access
Mode (CAM), Maximum Power Save, and Fast Power Save.












































