© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2005. All rights reserved.
User manual
Rev. 03 — 7 June 2005
83 of 139
Philips Semiconductors
UM10119
P89LPC938 User manual
12.6.4 Slave Transmitter mode
The first byte is received and handled as in the Slave Receiver Mode. However, in this
mode, the direction bit will indicate that the transfer direction is reversed. Serial data is
transmitted via P1.3/SDA while the serial clock is input through P1.2/SCL. START and
STOP conditions are recognized as the beginning and end of a serial transfer. In a given
application, the I
2
C-bus may operate as a master and as a slave. In the slave mode, the
I
2
C hardware looks for its own slave address and the general call address. If one of these
addresses is detected, an interrupt is requested. When the microcontrollers wishes to
become the bus master, the hardware waits until the bus is free before the master mode is
entered so that a possible slave action is not interrupted. If bus arbitration is lost in the
master mode, the I
2
C-bus switches to the slave mode immediately and can detect its own
slave address in the same serial transfer.
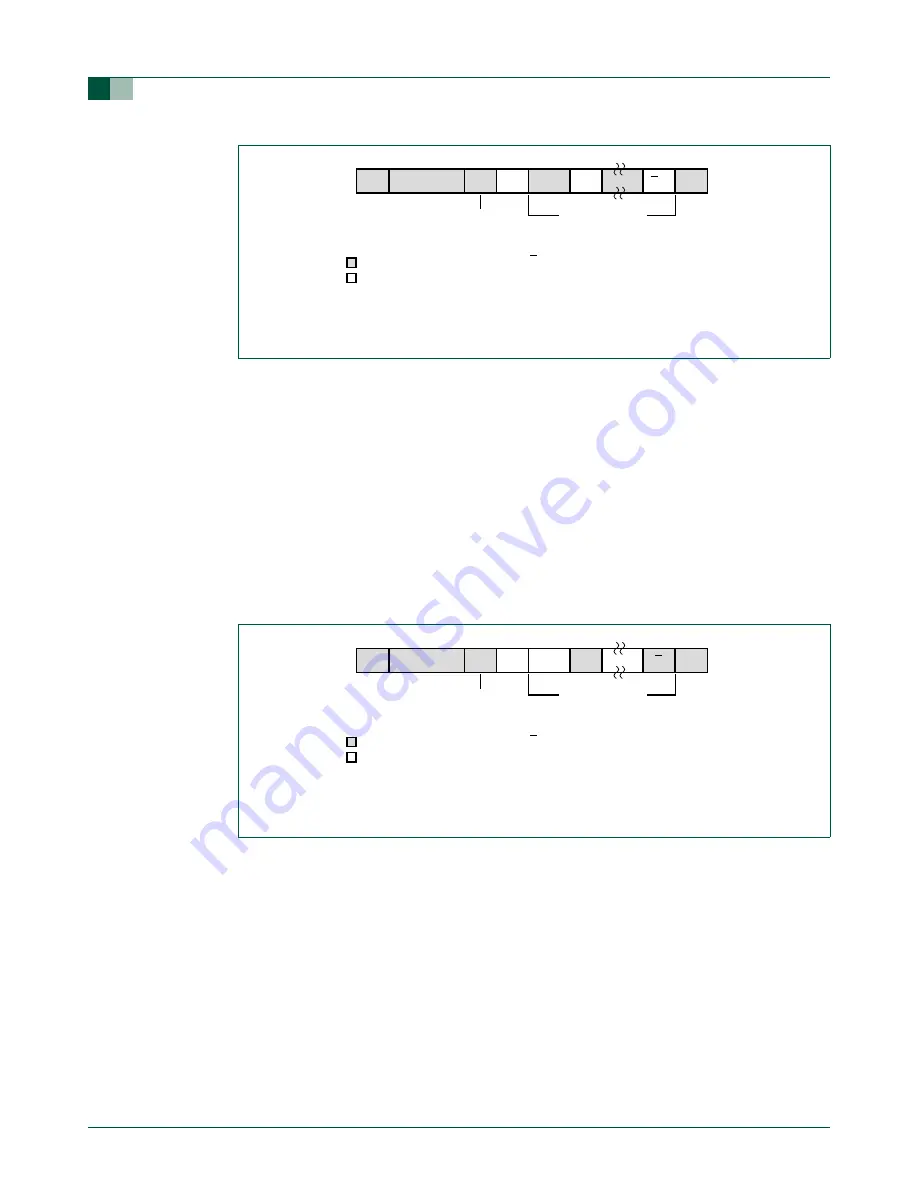
Fig 35. Format of Slave Receiver mode.
S
W
A
slave address
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
from Master to Slave
from Slave to Master
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
P = STOP condition
RS = repeated START condition
002aaa932
DATA
DATA
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
A
A/A
P/RS
Fig 36. Format of Slave Transmitter mode.
S
R
A
slave address
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
from Master to Slave
from Slave to Master
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
P = STOP condition
002aaa933
DATA
DATA
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
A
A
P
















































