Functional Safety KCD2-RR2-Ex1(.SP)
Operation
20
19
-1
1
15
Proof Test Procedure
1. Put out of service the entire safety loop. Protect the application by means of other measures.
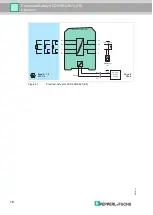
2. Connect a current source to terminals 7 and 8, see figure. Depending on the application,
the current source should supply 200
µ
A to 10 mA.
3. Connect a RTD simulator, see figure. Configure the device via the DIP switch according
to the application.
• For 4-wire connection: to terminals 1, 2, 3 and 4, DIP switch S1 in position II
• For 3-wire connection: to terminals 2, 3 and 4, DIP switch S1 in position I
• For 2-wire connection: to terminals 2 and 4, DIP switch S1 in position II
4. Secure the DIP switch to prevent unintentional adjustments. Close the cover.
5. Connect the digital multimeter to terminals 7 and 8, see figure.
6. Set the combinations of excitation currents and resistances, see table.
Use the current source and the RTD simulator.
The proof test is passed if the following voltage values are measured, see table.
7. To test the correct lead breakage detection, open the connections at
terminals 1, 2, 3 and 4
individually
.
The proof test is passed if the resistance signaled on the digital multimeter
for all excitation currents is between < 15
or > 400
.
The proof test is passed if the resistance signaled on the digital multimeter
for a excitation current < 1 mA is between < 15
or > 4 k
.
8. To test the correct lead breakage detection, open
all
connections at
terminals 1, 2, 3 and 4.
The proof test is passed if the resistance signaled on the digital multimeter
for all excitation currents is between < 15
or > 400
.
The proof test is passed if the resistance signaled on the digital multimeter
for a excitation current < 1 mA is between < 15
or > 4 k
.
9. Set back the device to the original settings for the application after the test.
Resistance
Excitation current
200
A
1 mA
10 mA
100
0.02 V
±
1.25 mV
0.1 V
±
0.25 mV
1 V
±
2.5 mV
400
0.08 V
±
5 mV
0.4 V
±
1 mV
4 V
±
10 mV
1 k
0.24 V
±
15 mV
1.2 V
±
3 mV
–
4 k
0.8 V
±
50 mV
4 V
±
10m V
–
Table 5.1
Resistance values, excitation currents and resulting voltages to test correct operation