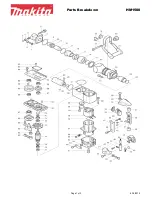
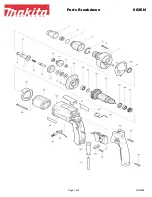
4.2 Operation
4.2.1 Constant voltage (CV) and constant current (CC)
The power supply acts as a constant voltage source (CV) as long as the load current is less than
the preset current limit. When the load current is greater than or equal to the preset current limit, the
power supply automatically switches to Constant mode, the voltage drops, (CC) is displayed on the
LED display panel and it operates as a constant current source.
When the load current falls below the preset current limit, the power returns to the constant voltage
(CV) mode.
4.2.2 Presetting the current limit value (CC)
If necessary, switch off the output with the Output button (6) until the symbol appears. Press the I
button (5) to select the current until one digit of the power indicator flashes. If necessary, press the
rotary control (11) to change the position to be changed. Now turn the knob (11) until the desired
maximum current value for your application is shown in the display. If you now switch on the output
with the output button (6), the current display changes from the set maximum value to the actual
value.
Note: A connected load only uses the actual required current, which may be less than what you set.
You can not force a load to consume more power than you actually need.
4.2.3 Connection and operation procedures
After comparing the voltage values with the nameplate, plug in the mains plug.
Turn on the power and the LCD should come on at the same time.
The symbol (CV) should be shown on the display.
If you do not need a lower current limit, set the desired output voltage and connect your load on the
jacks positive to positive and negative to negative.
Turn on the output and check if the display shows (CV).
If the display shows (CC), either your preset current limit is too low or your load requires more
voltage and current. You must re-access the voltage and current requirements of your load and
increase the voltage or current accordingly (CV), otherwise the power supply will be in the CC
current limit.
4.2.4 Overvoltage protection of the output (OVP)
This is to protect the connected load in the event of a malfunction of the output voltage control
circuit. The maximum output voltage at the time of operation will not exceed 30% of the set voltage
value.
- 9 -