®
Technical Support
PS
-
3202
11
013-14710C
15. Click Finish.
Theory of Calibration
One of the functions of the PASCO Data Collection
Software is to take the stream of raw data from a sensor
and transform it into the calibrated data that you see in
the Graph, Table, and other displays. If you do not
calibrate a sensor yourself, the software uses a default
calibration that is loaded when the sensor is connected.
You can think of the software as taking in raw data and
outputting calibrated data. When you perform a
calibration, the software redefines the linear equation
that transforms the raw input data into the calibrated
output data. The linear function is of the form:
Raw Input = Slope x Calibrated Offset
Or:
Calibrated Output = (Raw Input - Offset)/Slope
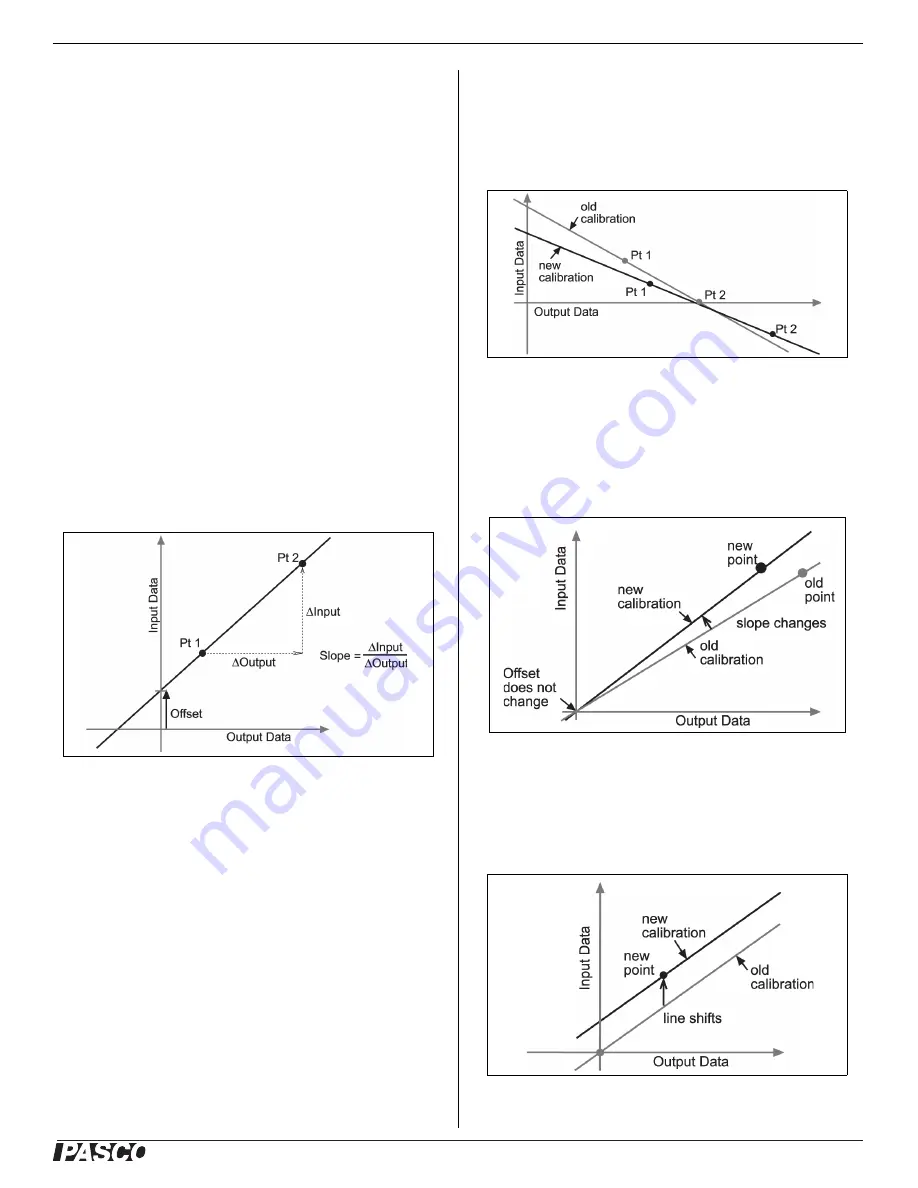
The function can be represented graphically as a line.
Two points, Pt 1 and Pt 2, define the line. In the
two-point calibration procedure, each point is reset by
associating a known standard value (for instance, the
temperature of ice water) with a raw input measurement
that the sensor sends out when it is in that standard. In a
one-point calibration, only one of the points is reset by
the user.
Types of Calibration
There are three types of calibration: two-point, one-point
slope, and one-point offset. Any of these calibrations can
be performed on a single sensor, or simultaneously on
multiple similar sensors; however, for any given sensor,
the software will automatically select the most typical
calibration type as the default setting.
Two-Point
In a two-point calibration, you reset two points to define
a new line. This type of calibration affects both the slope
and the offset.
One-Point Slope
In a one-point slope calibration, you reset only one point.
The slope of the line changes so that the line intersects
the new point, while the offset (or Y-intercept) does not
change.
One-Point Offset
In a one-point offset calibration, you reset only one point.
The line shifts so that it intersects the new point, but its
slope does not change.






























