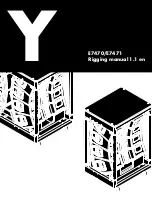
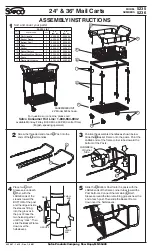
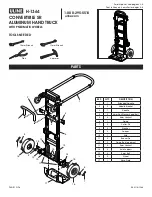
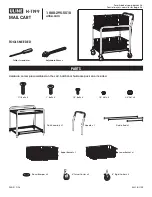
®
V a r i a b l e S p e e d M o t o r i z e d C a r t
ME-9781
6
Track the position versus time of the Variable Speed Motorized Cart and the
Fan Cart using two Rotary Motion Sensors and Track String Adapters. See Fig-
ure 8 for an example of typical experimental results.
Alternatively, collect data on the Variable Speed Motorized Cart using the
Rotary Motion Sensor and Track String Adapter, and then collect data on the
Fan Cart using a Time Pulse Accessory set to the same time interval. In this
manner, both runs can be plotted on the same graph display showing the differ-
ence in position versus time for constant acceleration and constant velocity.
Variable Force versus Efficiency (Constant Angle of Incline)
Explore the relationship between varying force and efficiency when a Variable
Speed Motorized Cart is climbing a track inclined at 30°. Use the Rotary
Motion Sensor and a Track String Adapter to measure the position of the cart
as it climbs the incline track (see Figure 9).
Vary the voltage supplied to the Variable Speed Motorized Cart with a “ramp down” signal from the 750
ScienceWorkshop
Inter-
face and Power Amplifier or the 850
Universal Interface
.
Manifest Different Voltage Wave Forms
Explore the effect of controlling the Variable Speed Motorized Cart with a variety of voltage wave forms (such as sine wave,
square, triangle, ramp up, ramp down, etc.) from the PASCO Interface. Plot the voltage and the position of the cart or the voltage
and the speed versus time.
Independence of Kinetic Friction and Speed
Determine the effect of speed on kinetic friction with a Force Sen-
sor mounted on the Variable Speed Motorized Cart. Place a fric-
tion block on a track and put two PASCO carts
accessory-tray-down on top of the friction block. Use the Force
Sensor to measure the kinetic friction (see Figure 10).
Figure 8: Typical Data
constant
acceleration
constant
velocity
Variable Speed
Motorized Cart
Angle
Indicator
Track String
Adapter
To the
interface
Figure 9: Efficiency vs Varying Force
Figure 10: Kinetic Friction and Speed
To the
interface
To the
voltage
source
Force
Sensor
PASCO
Carts (2)
friction
block
Motorized
Cart