3
Stainless Steel Brake Motors
P1V-S
Brake motor
Brake motors
Applications
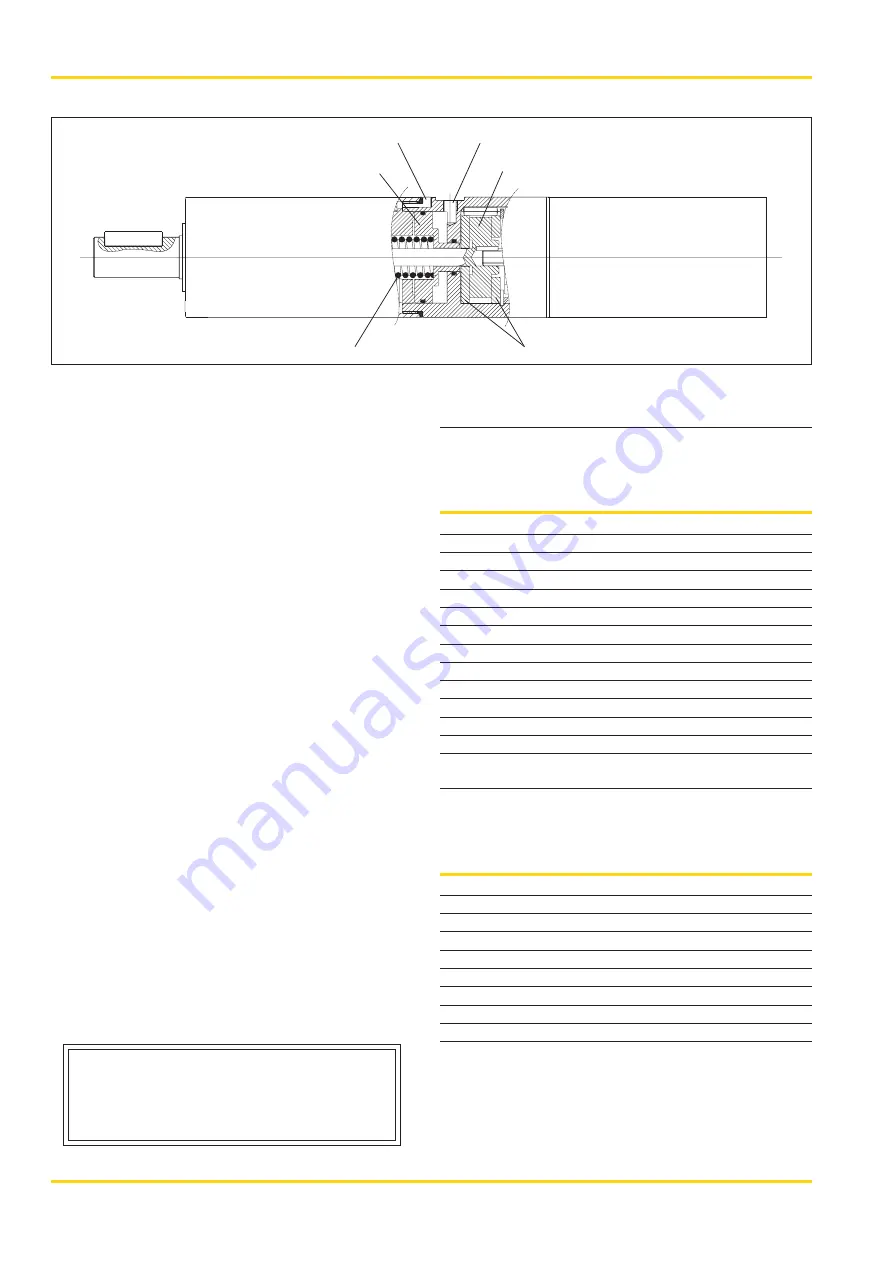
The integrated brake is a spring-loaded disk brake, which is released
at a minimum air pressure of 5 bar. The brake is applied in the
absence of pressure. As soon as the control port for the brake is
placed under pressure, the piston (1) is pressurised and the spring ()
is compressed. The motor can now start and the torque is passed to
the shaft (3). The ventilation air from the brake is connected with the
atmosphere. In order to brake the motor, the control air to the brake is
simply vented. The piston (1) is pushed to the right by the spring (),
and the axle (3) is jammed between the two brake disks (4).
The technology and the size of air motors with integrated running and
stationary brake make them ideal applications requiring repeated
precise positioning. The motor can also be kept stationary in a
specific position, and the stopping time for a rotating weight can be
shortened significantly. Another typical application for brake motors is
when the output shaft needs to be held in one position when the motor
stops delivering torque. The brake can handle more than 1500 braking
operations per hour at maximum braking torque.
Disassembly and reassembly
Detach the connections with the motor and gearbox. Pull off the motor
and gearbox part. The brake disks can be lifted off after the lock ring
has been removed.
Service and maintenance
After 0 000 braking operations as a stationary brake or 10 000
braking operations as an operating brake, the brake must be
disassembled in order to check for wear.
Warning:
If the number of braking operations is exceeded, the degree of wear
might be greater than permitted and the braking effect might be lost. If
this happens, you simply need to replace the worn brake linings. Tests
show that the brake lining needs to be replaced after approx. 90 000
braking cycles
Technical data
Min braking torque for different motor types
Motor size P1V-S00, 00 watt
Braking
Motor
Brake
Gearbox
motor
max
min braking
max
torque,
torque,
torque,
specified
theoretical
permitted
Nm
Nm
Nm
P1V-S00A/DDE50 0,5
1,0
1,0
P1V-S00A/DD460
1,6
3,43
3,43
P1V-S00A/DD40
3,
6,66
6,66
P1V-S00A/DD140
5,4
11,8
11,8
P1V-S00A/DD070 10,8
,86
14,0
P1V-S00A/DD035 0,0
44,4
0,0
P1V-S00A/DD018 0,0
44,4
0,0
P1V-S00A/D011
66,0
137,
108,0
P1V-S00A/D006
144,0
66,4
108,0
P1V-S00A/DD005 0,0*
44,4
0,0
P1V-S00A/D00
0,0*
44,4
0,0
P1V-S00A/D001
0,0*
44,4
0,0
P1V-S00A/D0005
0,0*
44,4
0,0
Motor size P1V-S030, 300 watt
Braking
Motor
Brake
Gearbox
motor
max
min braking
max
torque,
torque,
torque,
specified
theoretical
permitted
Nm
Nm
Nm
P1V-S030A/DDE50
0,8
1,0
1,0
P1V-S030A/DD460
,4
3,43
3,43
P1V-S030A/DD40
4,8
6,66
6,66
P1V-S030A/DD140
8,
11,8
11,8
P1V-S030A/DD060 19,
0,6
14,0
P1V-S030A/DD08 41,0
40,0
36,0
P1V-S030A/D03
48,0
70,8
108,0
P1V-S030A/D010
114,0
13,6
108,0
P1V-S030A/DD005 36,0*
40,0
36,0
* Warning:
The permitted torque for the specific gearbox must not be exceeded!
Brake release
Minimum pressure for brake release:
5 bar
1. Piston
Vent for motor brake
Control port for motor
brake
3. Shaft
. Compression spring
4. Brake disks
NOTE!
Brake motors must only ever be supplied with unlubricated
air, otherwise there is a risk of oil from the supply air getting
into the brake unit, resulting in poor brake performance or
no braking effect.
Summary of Contents for P1V-S002A0130
Page 66: ...66 Stainless Steel Air Motors P1V S...
Page 67: ......
















































