1752 and 1754 SHDSL Router User’s Guide
page. Check the interface details, then click on the
Delete
button.
Configuring NAT
To configure NAT, you need to:
1. Enable Security; see the
Enabling Security
section.
2. Create at least two different security interface types based on existing LAN services; see
the
Configuring Security Interfaces
section
.
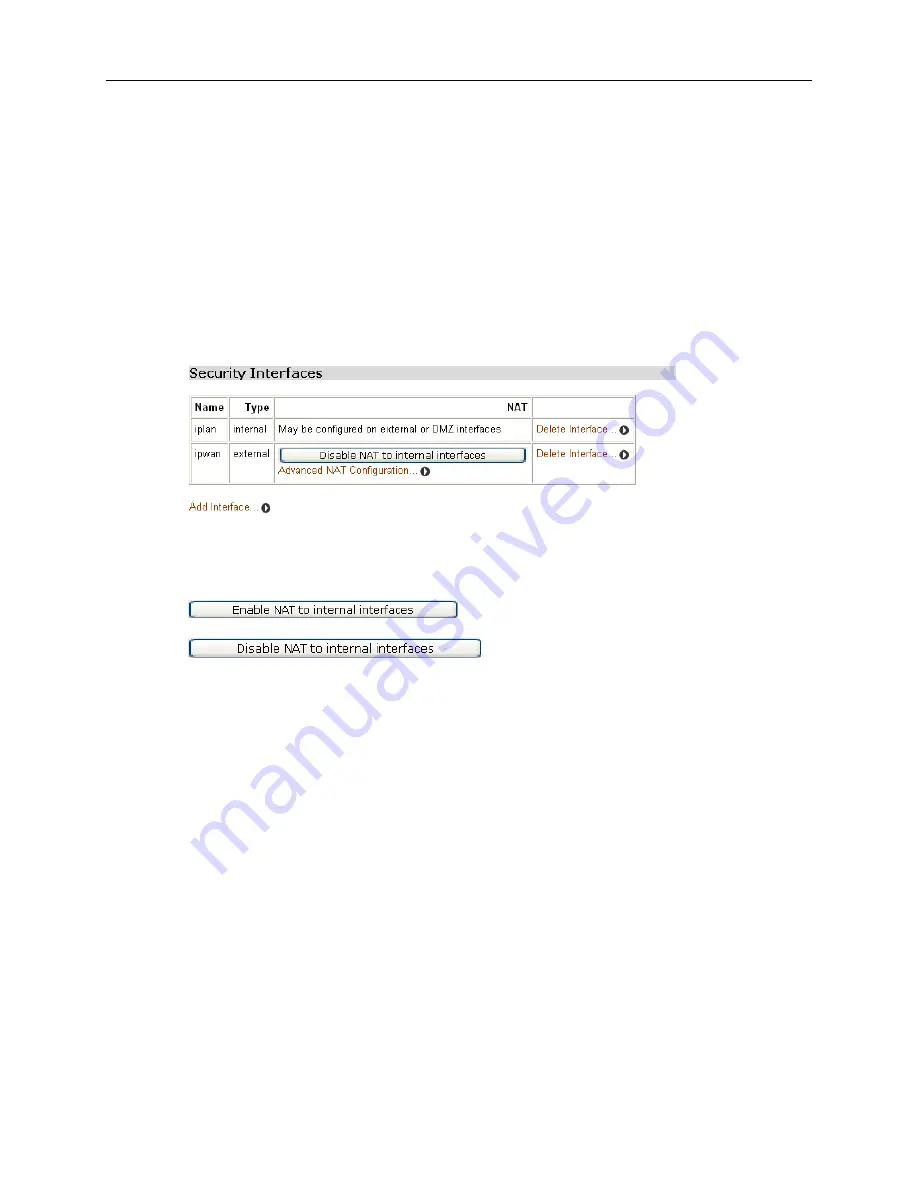
Once you have created more than one security interface, the
NAT
column in the
Security
Interfaces
table tells you that you can enable NAT between the existing security interface and
a network interface type. For example, if you create an external interface and an internal
interface, your table will look like this:
The NAT column for the external interface tells you that you can enable NAT to internal
interfaces. If you also had a DMZ interface configured, this column would also include an
Enable NAT to DMZ interfaces
button.
4. To enable NAT between the external interface and the internal interface type, click on
. The
Security
page is refreshed and NAT is enabled.
To disable NAT between these interfaces, click on
.
Once you have enabled NAT between interfaces, you can:
• Configure global addresses; see the
Configuring NAT global addresses
section.
• Configure reserved mapping; see the
Configuring NAT reserved mapping
section.
Configuring NAT Global Addresses
Global address pools allow you to create a pool of outside network addresses that is visible
outside your network. Before you can configure global addresses, you need to configure NAT.
See
Configuring NAT
Section
If you want to set up a global address pool on your existing NAT enabled interfaces:
1. From the
NAT Security Interfaces
table, click on the
Advanced NAT Configuration
hyperlink for the interface that you want to add a global pool to. The following page is
displayed:
1752-A2-GB20-00 June 2005
55






























