it is very helpful to use a precision collimating tool containing
crosshairs, such as the Orion Collimating Eyepiece (#3640).
We highly recommend that you purchase one.
Aligning the Secondary Mirror
With the eyepiece removed, look straight down the open
focuser drawtube at the secondary (diagonal) mirror. Ignore
the reflections for the time being. The secondary mirror
should be centered in the field of view. If it isn’t, as in Figure
8b, it must be adjusted. (It helps to adjust the secondary mir-
ror in a brightly lit room with the telescope pointed toward a
bright surface, such as white paper or a wall.)
If the secondary mirror is not centered in the focuser draw-
tube (in the direction parallel to the length of the telescope),
loosen the three set screws in the center hub of the sec-
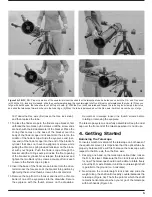
ondary mirror holder several turns. You will need a 3mm Allen
wrench to do this. Now hold the secondary mirror stationary
(be careful not to touch the surface of the secondary mirror!),
while turning the central Phillips head screw (as in Figure 9).
Turning the bolt clockwise will move the secondary mirror
toward the front opening of the optical tube, while turning the
bolt counterclockwise will move the secondary mirror toward
the primary mirror. When the secondary mirror is centered in
the focuser drawtube (as in Figure 8c), rotate the secondary
mirror holder slightly side-to-side until the reflection of the pri-
mary mirror is as centered in the secondary mirror as it will
get. It still may not be perfectly centered yet, but that is OK.
Now tighten the three set screws to secure the secondary
mirror in that position. This adjustment will rarely need to be
done, if ever.
If the entire primary mirror reflection is not visible in the sec-
ondary mirror (as it is not in Figure 8c), adjust the tilt of the
secondary mirror by alternately loosening one of the three set
screws a turn and tightening the other two (Figure 10). The
goal is to center the primary mirror reflection in the secondary
mirror, as depicted in Figure 8d. Don’t worry that the reflec-
tion of the secondary mirror (the smallest circle, with your eye
reflected in it) is off-center (as also is the case in Figure 8d);
you will fix that in the next step.
Adjusting the Primary Mirror
The final adjustment is made to the primary mirror. It will
need adjustment if, as in Figure 8d, the secondary mirror
is centered under the focuser and the reflection of the pri-
mary mirror is centered in the secondary mirror, but the
small reflection of the secondary mirror (with your eye
inside) is off-center.
The tilt of the primary is adjusted with the three pairs of colli-
mation screws on the back end of the optical tube (bottom of
the mirror cell, see Figure 11). The collimation screws can be
turned with a Phillips head screwdriver.
Each pair of collimation screws work together to adjust the
tilt. One screw pushes the mirror cell forward, while the other
screw pulls the mirror cell back. One must be loosened and
the other tightened by the same amount in order to adjust the
tilt. Try tightening and loosening one of the pairs of Phillips-
headed collimation screws one turn. Look into the focuser
and see if the secondary mirror reflection has moved closer
to the center of the primary mirror reflection. Repeat this
process on the other two pairs of collimation screws, if nec-
essary. It will take a little trial and error to get a feel for how
to tilt the mirror in this way to center the reflection. (It helps to
11
Figure 10. Adjust the tilt of the secondary mirror by loosening or
tightening the three alignment setscrews with a Phillips screwdriver.
Figure 9. To center the secondary mirror under the focuser, hold the
secondary mirror holder in place with one hand while adjusting the
center bolt with a Phillips screwdriver. Do not touch the mirror’s surface!
Figure 11. The back end of the optical tube (bottom of the primary
mirror cell). The three pairs of collimation screws adjust the tilt of the
primary mirror.