ENANCER Electrónica S.A.
Page 4 of 9
Rua Max Grundig 9
4705-820 Braga Portugal [email protected]
Tel: +351 253 221 484 www.only-smartbuildings.com
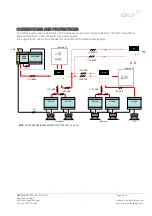
ARCHITECTURE OF THE INSTALLATION
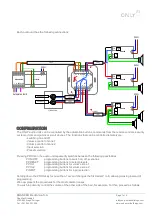
Generally, an audio system pretends to distribute the sound of a local or central source to any part of the house.
The distribution of a source to the rest of the house is very critical from the standpoint of cable and noise which
can be “caught” by the sound installation.
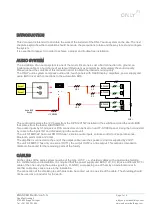
Sound distribution in star form
The sound distribution of the central source to the other units must be done as a “star”, this means that
a cable must be connected from the source to each unit in the house, and never a cable connecting one
unit with the other and so on.
The previous rule is critical to avoid background noise. If not, the noise from the digital part of a unit will be
audible in the next unit, resulting in an annoying background noise in sound, even with the volume set to zero.
It is suggested therefore that not only the distribution of the sound signal, but also of the power and BUS is made
using the same architecture.
For the distribution of sound through the house it is necessary to understand that a sound source (e.g. CD player)
provides a certain electric current (I1) when connected to a sound unit.
So, if we increase the number of audio units connected to the same source, we are increasing the current we are
asking for at input. As the source has a certain impedance R, we have a voltage drop.
V = I x R
That is, if we have 3 audio units we have three times more loss at the source than if we had only one unit.
This loss is imperceptible for a few units (3 or 4), because normally the input impedance of the audio units is
much higher than the output impedance of the source (typically a ratio 1:10).
When more units are used, this loss causes distortion that starts to be audible in the sound.
This effect almost disappears if the output impedance of the source is very low. This lowering is achieved using
an intermediate unit equipped with a line buffer.
The good news is that all ONLY audio units are equipped with these line buffers, no matter if they are regulated or
line level.
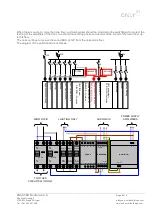
In general, a normal audio source (e.g. CD player) can feed up to 4 ONLY audio units without significant quality
loss. For more than this, a C-FMBT-C unit should be used as a central, distributing its line output (OUT2) to the
other units in the facility. This way the central unit provides the selected audio source to the rest of the facility.
I1
I1
I1
3xI1
R
V
Central
Summary of Contents for Audio
Page 1: ...Audio Installation Manual ...