144
Response Codes
Section 6-6
6-6-1
Configuration
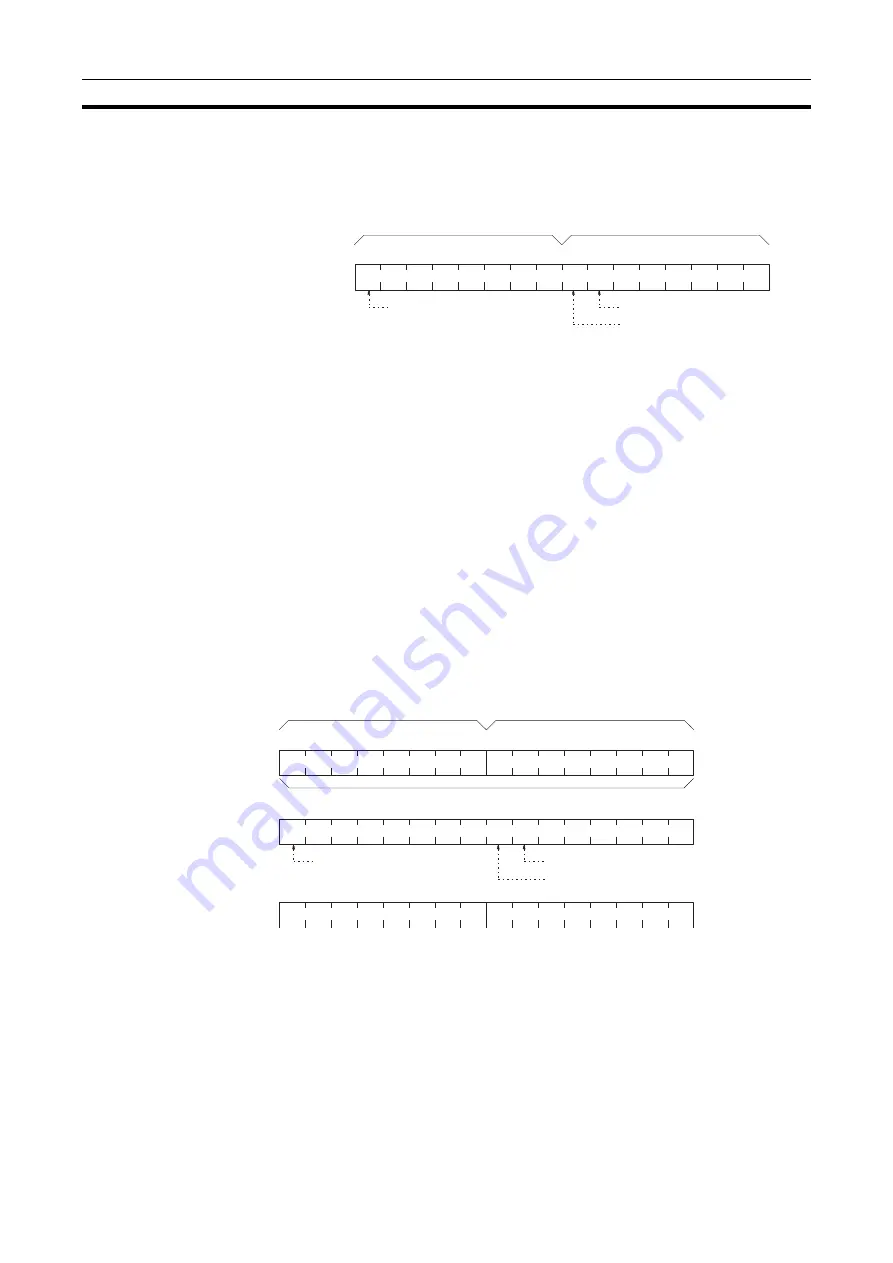
Response codes for FINS commands consist of two bytes that indicate the
result of executing a command. The structure of the response codes is shown
in the following diagram.
The main response code (MRES) in the first byte classifies the response and
the sub-response code (SRES) in the second byte indicates details under the
MRES classification.
If bit 7 of the first byte is ON, a network relay error has occurred. Refer to 6-6-
2 Network Relay Errors for details on troubleshooting the error.
If bit 6 or 7 of the second byte is ON, an error has occurred in the PLC or com-
puter returning the response. Refer to the operation manual for the device
returning the response for details when troubleshooting the error.
6-6-2
Network Relay Errors
A network relay error will occur whenever a command cannot reach the desti-
nation. These errors can occur for several reasons: 1) Data was not success-
fully passed between two Link Units, 2) Data was not passed successfully
between a Link Unit and another Unit, such as the PLC’s CPU Unit, or 3) The
destination of a gateway does not exist. In any case, the Unit that was not able
to transfer data will return a response indicating a network relay error.
Bit 7 of the first byte of the response code will be ON if a network relay error
has occurred. When this happens, two more bytes of data will follow the
response code to indicate the location of the error. This information, along
with the response code, should enable you to track the error.
Error network address: 00 to 7F (Hex) (0 to 127 in decimal)
Error node address:
Controller Link: 01 to 3E (Hex) (1 to 62 in decimal) (*1)
Ethernet:
01 to 7E (Hex) (1 to 126 in decimal)
SYSMAC NET: 01 to 7E (Hex) (1 to 126 in decimal)
SYSMAC LINK:01 to 3E (Hex) (1 to 62 in decimal)
*1 This is 01 to 20 Hex (1 to 32) for Wired or Optical
Bus (CLK11) Controller Link Units.
Relay Errors
A relay error indicates that the command did not reach the Unit to which it was
sent. There are several types of situation in which this can occur. Example 1
(below) shows a situation in which a relay error occurs when data cannot be
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Bit
1: PLC Non-fatal Error Flag
1: PLC Fatal Error Flag
1: Relay Error Flag
First byte
Second byte
Main response code (MRES) Sub-response code (SRES)
Bit
1: PLC Non-fatal Error Flag
1: PLC Fatal Error Flag
Error network address Error node address
0 0 0
First word
Second word
Third word
Command code
1: Relay Error Flag
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
First byte
Second byte
Main response code (MRES) Sub response code (SRES)
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Summary of Contents for CS1W-CLK12-V1
Page 3: ...iv ...
Page 5: ...vi ...
Page 9: ...x TABLE OF CONTENTS ...
Page 11: ...xii ...
Page 59: ...42 Component Names and Functions Section 3 1 Dimensions Unit mm ...
Page 62: ...45 Component Names and Functions Section 3 1 Dimensions Unit mm ...
Page 91: ...74 CVM1 and CV series Optical Ring Controller Link Units Section 4 2 ...
Page 108: ...91 Setting Data Links Section 5 2 Device Information Setting Data Link Tables ...
Page 125: ...108 Checking Data Link Status Section 5 4 ...
Page 181: ...164 Setting Routing Tables Section 7 4 ...
Page 199: ...182 Memory Areas Related to Duplex Operation Section 8 6 ...
Page 275: ...258 Handling Precautions Section 10 7 ...
Page 298: ...281 CS series Optical Bus Controller Link Units Appendix C Dimensions Unit mm 101 35 130 ...
Page 299: ...282 CS series Optical Bus Controller Link Units Appendix C ...
















































