6
|
ni.com
|
NI SMD-7611/7612 User Manual
Voltage
The motor can provide more torque at higher speeds if a higher power supply voltage is used.
Refer to the
section for guidance.
If you choose an unregulated power supply, make sure the no load voltage of the supply does not
exceed the drive’s maximum input voltage specification.
Current
The maximum supply current you could ever need is two times the motor current. However, you
will generally need a lot less than that, depending on the motor type, voltage, speed and load
conditions. That’s because the NI SMD-7611/7612 uses a switching amplifier, converting a high
voltage and low current into lower voltage and higher current. The more the power supply
voltage exceeds the motor voltage, the less current you’ll need from the power supply. A motor
running from a 48 volt supply can be expected to draw only half the supply current that it would
with a 24 volt supply.
We recommend the following selection procedure:
1.
If you plan to use only a few drives, get a power supply with at least twice per phase current
rating of the step motor. Example: for a motor that’s rated for 2 A/phase use a 4 A power
supply.
2.
If you are designing for mass production and must minimize cost, get one power supply
with more than twice the rated current of the motor. Install the motor in the application and
monitor the current coming out of the power supply and into the drive at various motor
loads. This will tell you how much current you really need so you can design in a lower cost
power supply.
Tables 1 and 2 list the maximum current required for each motor at several common power
supply voltages. Please consider this information when choosing a power supply.
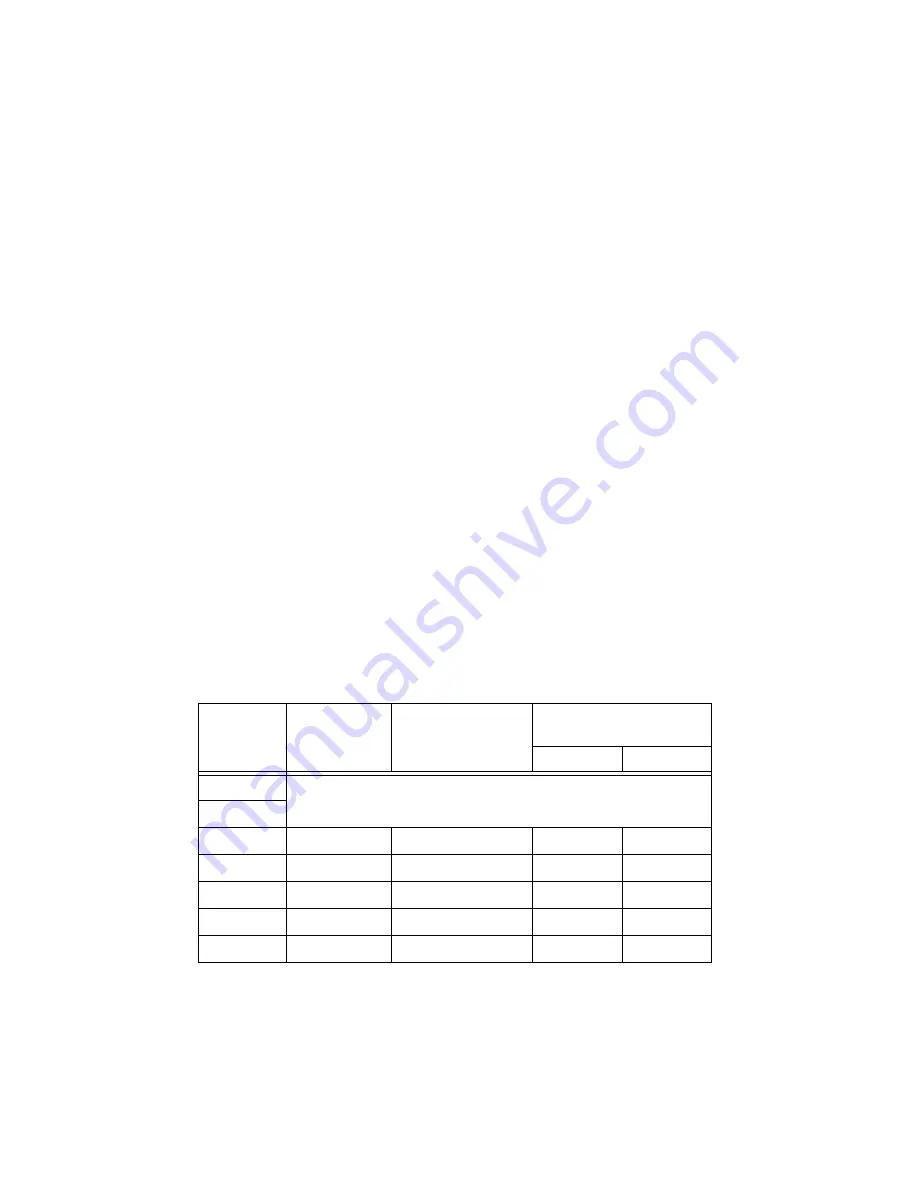
Table 1.
NI SMD-7611 Power Supply Current
Switch
Motor
Drive Current (A),
peak of sine
Max Power Supply
Current (A)
24 VDC
48 VDC
0
Reserved for
custom motors
1
2
ST17-4
2.4 parallel
1.6
1.7
3
ST17-1
1.6 parallel
1.1
1.1
4
ST17-2
2.0 parallel
1.1
1.1
5
ST17-3
2.0 parallel
1.1
1.1
6
ST23-1
3.4 parallel
1.9
2.0





















