NEC SL1100
Issue 6.0
Networking Manual
13 - 5
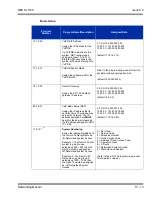
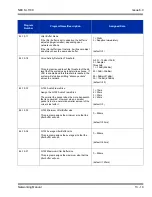
Below is a table that shows the average bandwidth per VoIP call over Ethernet.
For example, if one site plans on making a maximum of 16 calls across the network
using G.729 with a 30ms packet size, there must be a minimum of 376kbps available
for voice traffic. The QOS policy for this network should allow for 376kbps to be set
aside for voice prioritization.
S
ECTION
4
Q
UALITY
OF
S
ERVICE
S
ETTINGS
(QOS)
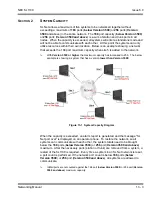
Quality of Service (QOS) is one of the most important factors for VoIP. QOS is used
to prioritize voice packets over data packets during times of network congestion.
There are many ways that QOS can be implemented in the network and one of the
most common ways QOS is implemented is by using IP Precedence or Diffserv. If the
networks QOS policy is based on IP Precedence or Diffserv then there are settings
required in the SL1100.
Program 84-10 is used to assign the IP Precedence or Diffserv Values per Protocol
Type. For SL Net only two protocol types will be selected. All signaling packets will
be marked with the values assigned for protocol type “H.323”. All voice packets will
be marked with the values assigned for protocol type “RTP/RTCP”.
S
ECTION
5
IP P
RECEDENCE
IP Precedence uses the first 3 bits of the TOS field to give eight possible precedence
values (0 ~ 7). Under normal circumstances the higher the number the higher the
priority. However this is left to the network administrator for setup. When assigning IP
Precedence values (for SL Net) go to program 84-10-01 and change the type from
Disabled to IP Precedence. Then in program 84-10-02 assign the value for the
Table 13-1 Bandwidth per VoIP Call
Codec
Packet Size
Bandwidth
Used
Codec
Packet Size
Bandwidth
Used
G.711
10ms
110.4kbps
G.729
10ms
54.4kbps
G.711
20ms
87.2kbps
G.729
20ms
31.2kbps
G.711
30ms
79.5kbps
G.729
30ms
23.5kbps
G.711
40ms
75.6kbps
G.729
40ms
19.6kbps
G.722
10ms
110.4kbps
G.729
50ms
17.3kbps
G.722
20ms
87.2kbps
G.729
60ms
15.7kbps
G.722
30ms
79.5kbps
G.723
30ms
20.8kbps
G.722
40ms
75.6kbps
G.723
60ms
13.2kbps
Summary of Contents for SL1100
Page 1: ...Networking Manual NDA 31190 Issue 6 0 SL1100...
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 22: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 1 2 Introduction THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 62: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 5 30 Programming THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 94: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 6 32 Network Design Considerations THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 134: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 8 10 DHCP Client THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 159: ...NEC SL1100 Issue 6 0 Networking Manual 9 25 Figure 9 7 Log In to IP Phone...
Page 181: ...NEC SL1100 Issue 6 0 Networking Manual 9 47 Figure 9 25 IP System Operation Setup...
Page 206: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 9 72 IP Multiline Station SIP Figure 9 36 NAPT Configuration Example...
Page 230: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 10 18 IP Single Line Telephone THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 232: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 11 2 NAPT Figure 11 1 NAPT Configuration Example...
Page 242: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 12 4 All DSP Busy Indication THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 290: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 13 48 SL Net THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 291: ......
Page 292: ...SL1100 Networking Manual NEC Corporation of America Issue 6 0...