13
LA010065D
© 2004 Navman NZ Ltd. All rights reserved. Proprietary information and specifications subject to change without notice.
4.0 Hardware interface
The electrical interface of the Jupiter GPS receiver
is through a 20-pin header. The function of each
pin is described in table 5-1.
4.1 DC input signals
4.1.1 Pin J1-1: antenna preamp voltage input
(PREAMP)
This signal is used to supply an external voltage to
the GPS antenna pre-amplifier (no3.3 or
+5, max +12 VDC). Customer-provided antenna
current limiting protection will prevent damage to
the GPS receiver from external short circuits.
4.1.2 Pins J1-2 and J1-4: primary VDC power
input and (PWRIN)
Jupiter 12 supports 3.3 VDC and 5 VDC. The
main power must be regulated and have maximum
ripple of 50 mV. Note that pin 2 and pin 4 are
connected together, whereas previous Jupiter
versions were missing pin 2 or pin 4 depending
upon model voltage rating.
4.1.3 Pin J1-3: battery backup voltage input
(VBATT)
Jupiter boards contain SRAM (Static Random
Access Memory) and an RTC that can run on
backup power at low current if primary power is
removed. Start-up time is generally improved when
power is maintained to SRAM and RTC as the
data required to predict satellite visibility and to
compute precise satellite positions is maintained.
Battery backup is required for proper operation of
the DR receiver. During times when primary power
to the board is off, current is typically 12 µA.
4.1.4 Pin J1-5: master reset (M_RST)—active
low
This signal is the master reset, used to warm start
the receiver. This pin should be tied to a logic ‘high’
with a 47 kΩ resistor.
Note:
for receiver to operate normally, the M_RST
signal must be pulled to a CMOS logic ‘high’ level
coincident with, or after, application of prime DC
power to the receiver. The M_RST signal must
be held at ground level for a minimum of 1 µs to
assure proper generation of a hardware reset.
4.1.5 Pin J1-6: heading rate gyro input (GYRO)
This pin is used for the heading rate gyro input
on Jupiter TU35-D420 Jupiter 12 DR receivers.
Characteristics of the input signal are:
• 0 to 5 V range
• 2.5 V output when gyro is not being rotated
• clockwise rotation of the gyro causes
voltage to rise
• maximum voltage deviation due to rotation
should occur with a turning rate of 90
degrees/second or less
The gyro should be mounted so its sensitive axis is
as vertical as practical. Deviations from the vertical
reduce sensitivity for heading changes in the
horizontal direction. Acceptable performance can
be achieved with mounting deviations of several
degrees, but better performance is achieved when
the gyro is mounted closer to vertical. Contact
Navman for suggested sources for rate gyros.
4.1.6 Pin J1-7: NMEA protocol select/backup
(GPIO2)
This pin is used to receive an optional backup
signal from the vehicle on Jupiter TU35-D420
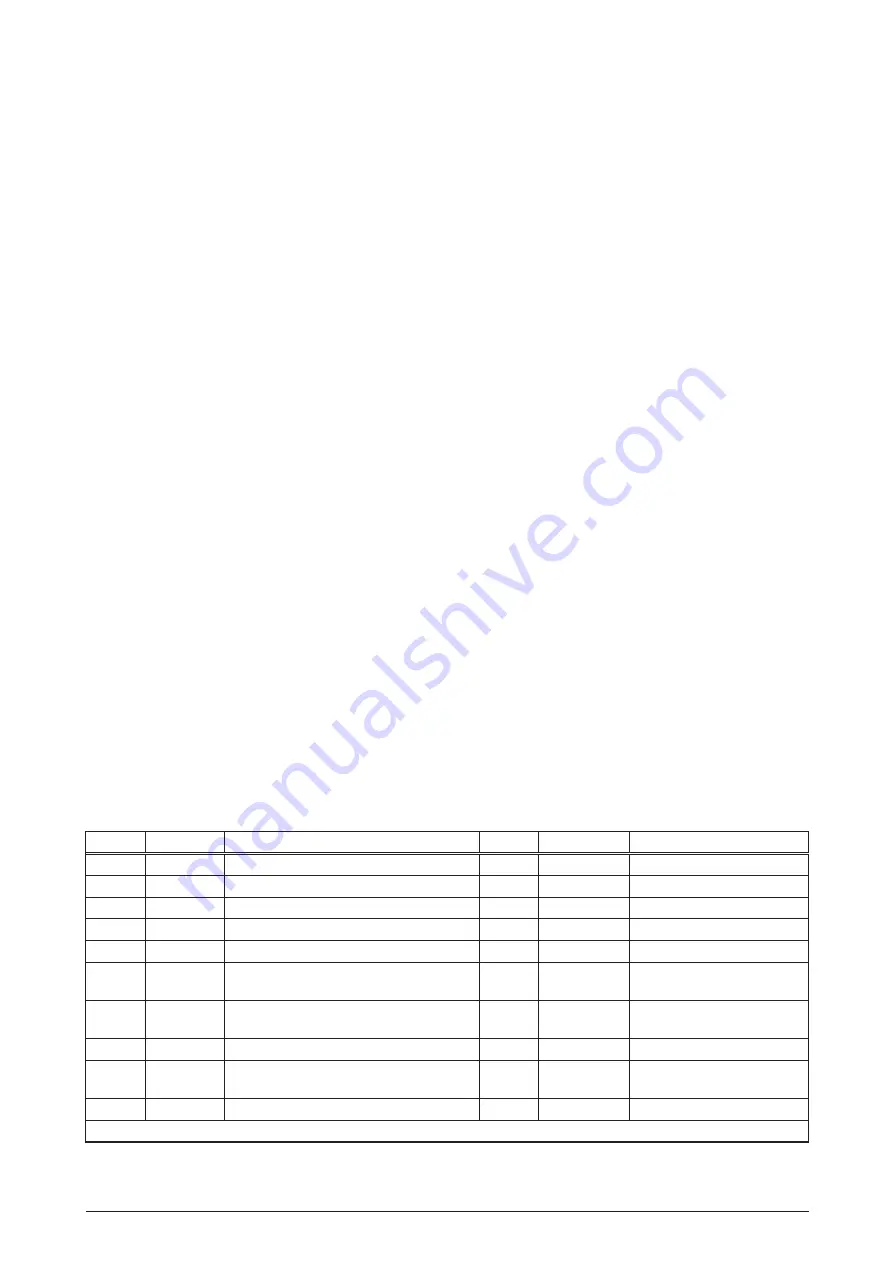
Pin No.
Name
Description
Pin No.
Name
Description
1
PREAMP antenna preamp voltage input
11
SDO1
serial data output port #1
2
PWRIN
primary VDC power input
12
SDI1
serial data input port #1
3
VBATT
battery backup voltage input
13
GND
ground
4
PWRIN
primary VDC power input
14
SDO2
serial data output port #2
5
M_RST
master reset input (active low)
15
SDI2
serial data input port #2
6
GYRO
DR heading rate gyro input otherwise
reserved (no connect) (Note 1)
16
GND
ground
7
GPIO2
NMEA protocol select
forward/reverse sensor (Note 1)
17
GND
ground
8
GPIO3
EEPROM default select
18
GND
ground
9
GPIO4
DR speed indication otherwise reserved
(no connect) (Note 1)
19
TMARK
1PPS time mark output
10
GND
ground
20
10 kHz
10 kHz clock output
Note 1: Pins 6, 7, and 9 have dual functions depending on the specific Jupiter receiver configuration.
Table 4-1 Jupiter receiver J1 interface pin descriptions




































