Chapter 4
Programming with NI-IMAQ for 1394 VIs
©
National Instruments Corporation
4-3
NI-IMAQ for IEEE-1394 Cameras User Manual
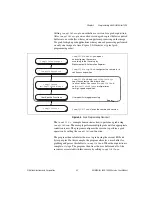
The most commonly used VIs are on the
IMAQ for IEEE-1394
palette.
You can find VIs for basic acquisition and changing attributes.
The
Motion and Vision»IMAQ for IEEE-1394»IMAQ Low Level
palette contains VIs for more advanced applications.
See the
NI-IMAQ for IEEE-1394 VI Reference help
for more information.
Common NI-IMAQ for 1394 VI Parameters
IMAQ1394 Session
is a unique identifier that specifies the Interface file
used for the acquisition. It is produced by the IMAQ1394 Init VI and used
as an input to all other NI-IMAQ VIs. The NI-IMAQ for 1394 VIs use
IMAQ1394 Session Out
, which is identical to
IMAQ Session
, to simplify
dataflow programming.
IMAQ1394 Session Out
is similar to the duplicate
file sessions provided by the file I/O VIs. The high-level acquisition
VIs—IMAQ1394 Snap, IMAQ1394 Grab Setup, and IMAQ1394
Sequence—require you to wire
IMAQ1394 Session In
only if you are
using an interface other than the default
cam0
, if you are using multiple
cameras, or if you need to set IMAQ 1394 properties before the acquisition.
Many acquisition VIs require that you supply an image buffer to receive the
captured image. You can create this image buffer with the IMAQ Create VI.
Consult the
section of this chapter for more
information. The input that receives the image buffer is
Image in
. The
Image out
output returns the captured image.
The acquisition VIs use the
Region of Interest
input to specify a
rectangular portion of an image frame to be captured. You can use
Region
of Interest
to reduce the size of the image you want to capture.
Region of
Interest
is an array of four elements with the elements defined as Left, Top,
Right, Bottom. If
Region of Interest
is not wired, the entire image
acquisition window is captured. You configure the default acquisition
window using MAX.
Note
The Region of Interest input is only used when your camera is configured to use
Scalable Image Format (format 7).