Chapter 1
Introduction
©
National Instruments Corporation
1-3
Inspection
Before you operate the GPIB-232CV-A, inspect the shipping container and
its contents for damage. Keep the packing material for possible inspection
and/or reshipment.
If the equipment appears to be damaged, do not attempt to operate it.
Contact National Instruments for instructions. If the damage appears to
have been caused in shipment, file a claim with the carrier.
GPIB-232CV-A Panels
The following sections describe the panels of the GPIB-232CV-A.
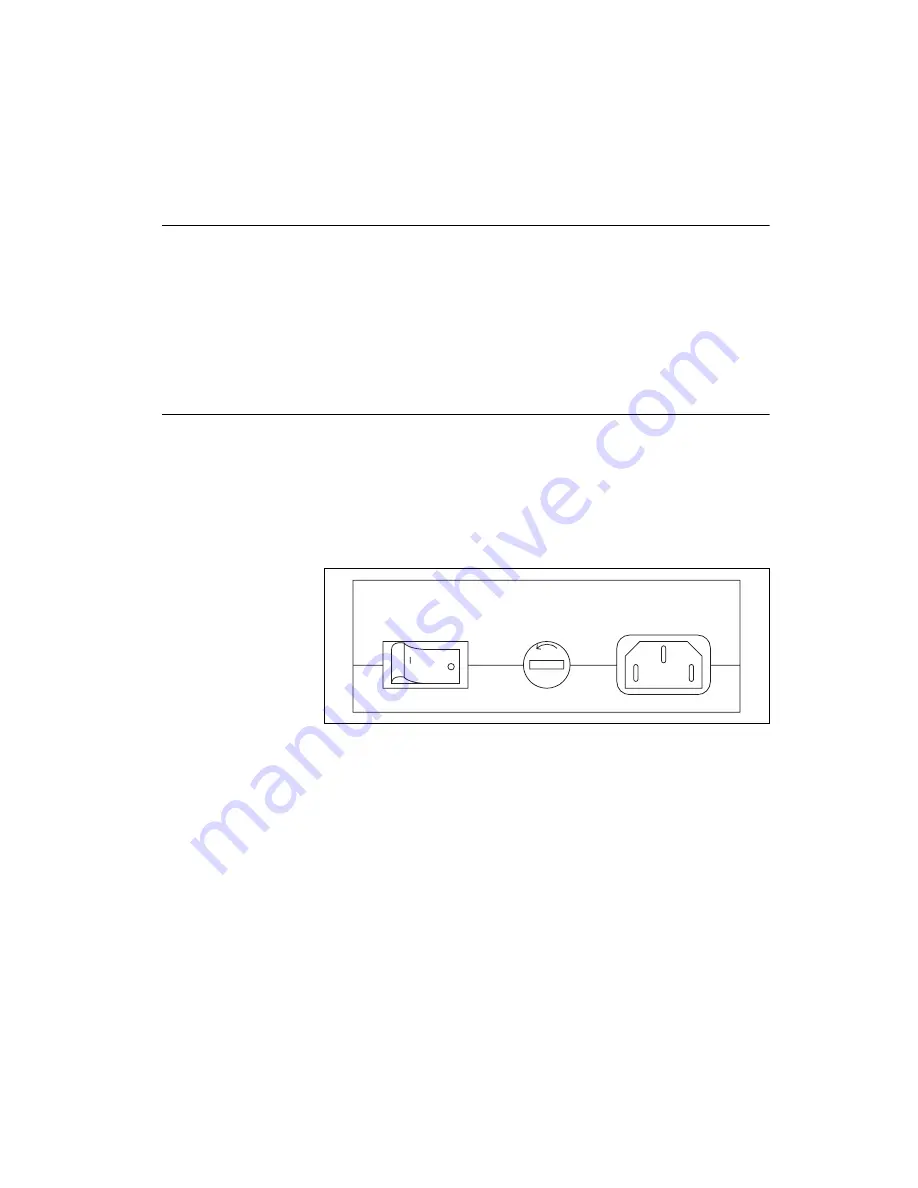
AC Front Panel
The power switch, fuse holder, and power cord receptacle are located on
the GPIB-232CV-A front panel, on the AC version only. Figure 1-1 shows
the front panel of the AC version.
Figure 1-1.
GPIB-232CV-A AC Front Panel
FUSE




























