MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
DSP56007
Order this document by:
DSP56007/D
©1996, 1997 MOTOROLA, INC.
SYMPHONY
AUDIO DSP FAMILY
24-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
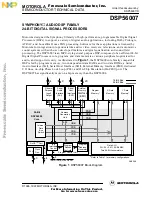
Motorola designed the Symphony
family of high-performance, programmable Digital Signal
Processors (DSPs) to support a variety of digital audio applications, including Dolby ProLogic,
ATRAC, and Lucasfilm Home THX processing. Software for these applications is licensed by
Motorola for integration into products like audio/video receivers, televisions, and automotive
sound systems with such user-developed features as digital equalization and sound field
processing. The DSP56007 is an MPU-style general purpose DSP, composed of an efficient 24-bit
Digital Signal Processor core, program and data memories, various peripherals optimized for
audio, and support circuitry. As illustrated in
, the DSP56000 core family compatible
DSP is fed by program memory, two independent data RAMs and two data ROMs, a Serial
Audio Interface (SAI), Serial Host Interface (SHI), External Memory Interface (EMI), dedicated
I/O lines, on-chip Phase Lock Loop (PLL), and On-Chip Emulation (OnCE
) port. The
DSP56007 has significantly more on-chip memory than the DSP56004.
ˇ
Figure 1
DSP56007 Block Diagram
Y Data
Memory*
X Data
Memory*
Program
Memory*
Program Control Unit
24-Bit
DSP56000
Core
OnCE
TM
Port
PLL
Clock
Gen.
4
9
5
29
16-Bit Bus
24-Bit Bus
Data ALU
24
×
24 + 56
→
56-Bit MAC
Two 56-Bit Accumulators
Interrupt
Control
Program
Decode
Controller
Program
Address
Generator
4
IRQA, IRQB, NMI, RESET
4
3
Internal
Data
Bus
Switch
Address
Generation
Unit
Refer to Table 1 for memory configurations.
*
PAB
XAB
YAB
GDB
PDB
XDB
YDB
General
Purpose
Input/
Output
External
Memory
Interface
(EMI)
Serial
Audio
Interface
(SAI)
Serial
Host
Interface
(SHI)
AA0248
F
re
e
sc
a
le
S
e
m
ic
o
n
d
u
c
to
r,
I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
n
c
.
..
Summary of Contents for NXP SYMPHONY DSP56007
Page 82: ......