Setting Parameters
01/02 AWB8230-1413GB
116
PID control
The DF6 frequency inverters have PID control as standard. This can
be used, for example, for flow and throughput controllers with
fans and pumps. PID control has the following features:
• The setpoint value can be issued through the frequency inverter
keypad or through an external digital signal (fixed frequencies).
Sixteen different setpoint values are possible. In addition, the
setpoint can be defined with an analog input signal (0 to 10 V
or 4 to 20 mA).
• With the DF6, the actual value signal can be fed back using an
analog input voltage (up to 10 V) or an analog input current (up
to 20 mA).
• The permissible range for the actual value signal feedback can
be specifically matched (e.g. 0 to 5 V, 4 to 20 mA, or other
ranges).
• With the aid of a scale adjustment, you can match the setpoint
signal and/or the actual value signal to the actual physical
quantities (such as air or water flow, temperature, etc.) and
view them on the display.
PID control
“P” stands for
p
roportional, “I” for
i
ntegral and “D” for
d
ifferential. In control engineering, the combination of these three
components is termed PID closed-loop control, PID regulation or
PID control. PID control is used in numerous types of application,
e.g. for controlling air and water flow or for controlling pressure
and temperature. The output frequency of the inverter is controlled
by a PID control algorithm to keep the deviation between the
setpoint and actual value as small as possible. The figure below
illustrates PID control in the form of a block diagram:
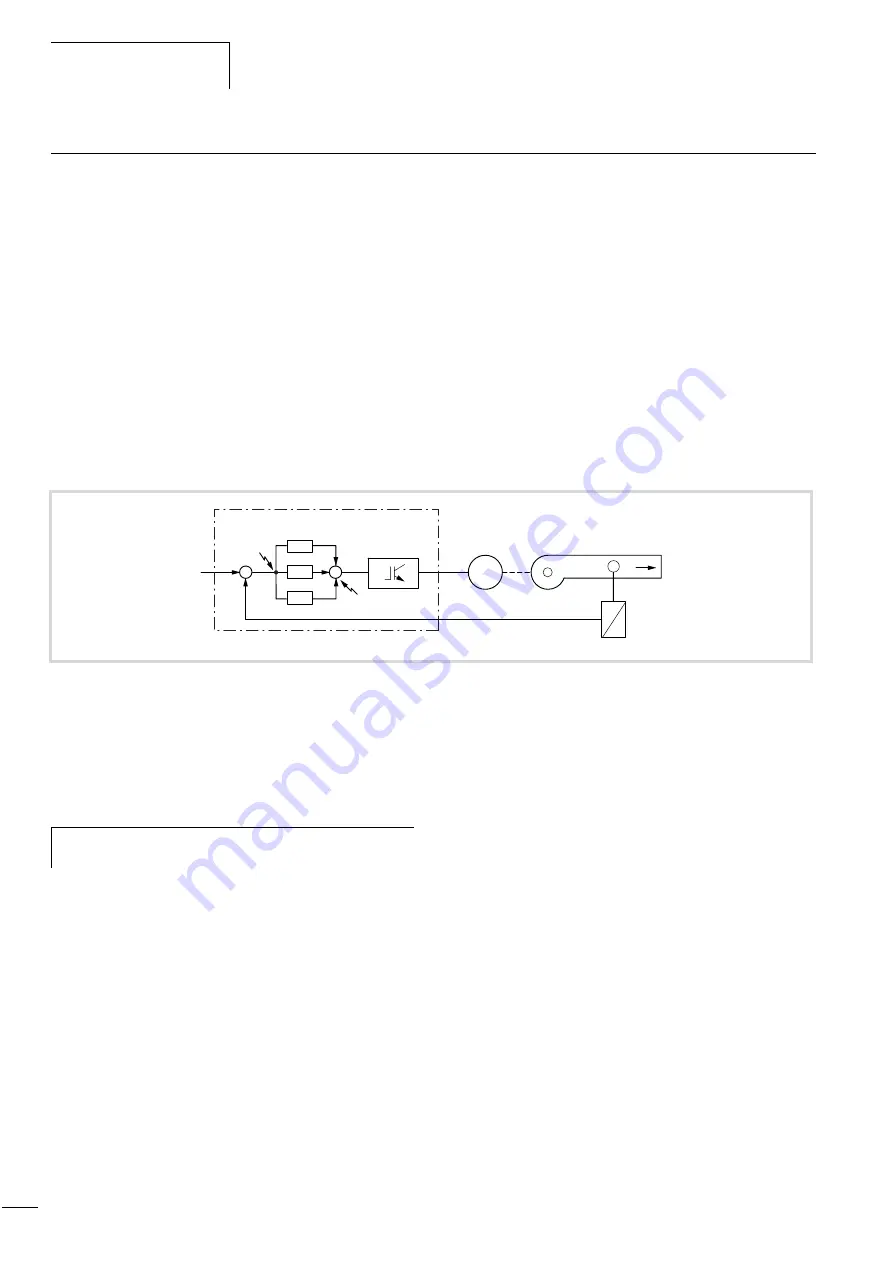
Figure 115: PID control block diagram
G1: DF6 frequency inverter
w: Setpoint
x: Actual value
P1: Controlled variable
B1: Measured value converter
a
System deviation
b
Inverter
c
Fans, pumps or similar devices
d
Frequency setpoint value
B1
P1
x
c
b
d
a
M
3
~
I
P
D
+
w
G1
+
–
+
+
h
PID control is only possible after the type of setpoint value
and actual value used have been defined.
efesotomasyon.com - Klockner Moeller - inverter
















































