60
3 MAJOR POSITIONING CONTROL
3.1 Overview of the Major Positioning Controls
*1 In 2-axis linear interpolation control, 3-axis linear interpolation control, 4-axis linear interpolation control, 2-axis fixed-feed control, 3-axis
fixed-feed control, 4-axis fixed-feed control, 2-axis circular interpolation control, 3-axis helical interpolation control, 2-axis speed control,
3-axis speed control, and 4-axis speed control, use a motor set for the directions of two or more axes to control the positioning drawing
a straight line or an arc path.
This type of control is called interpolation control. (
Page 77 Interpolation control)
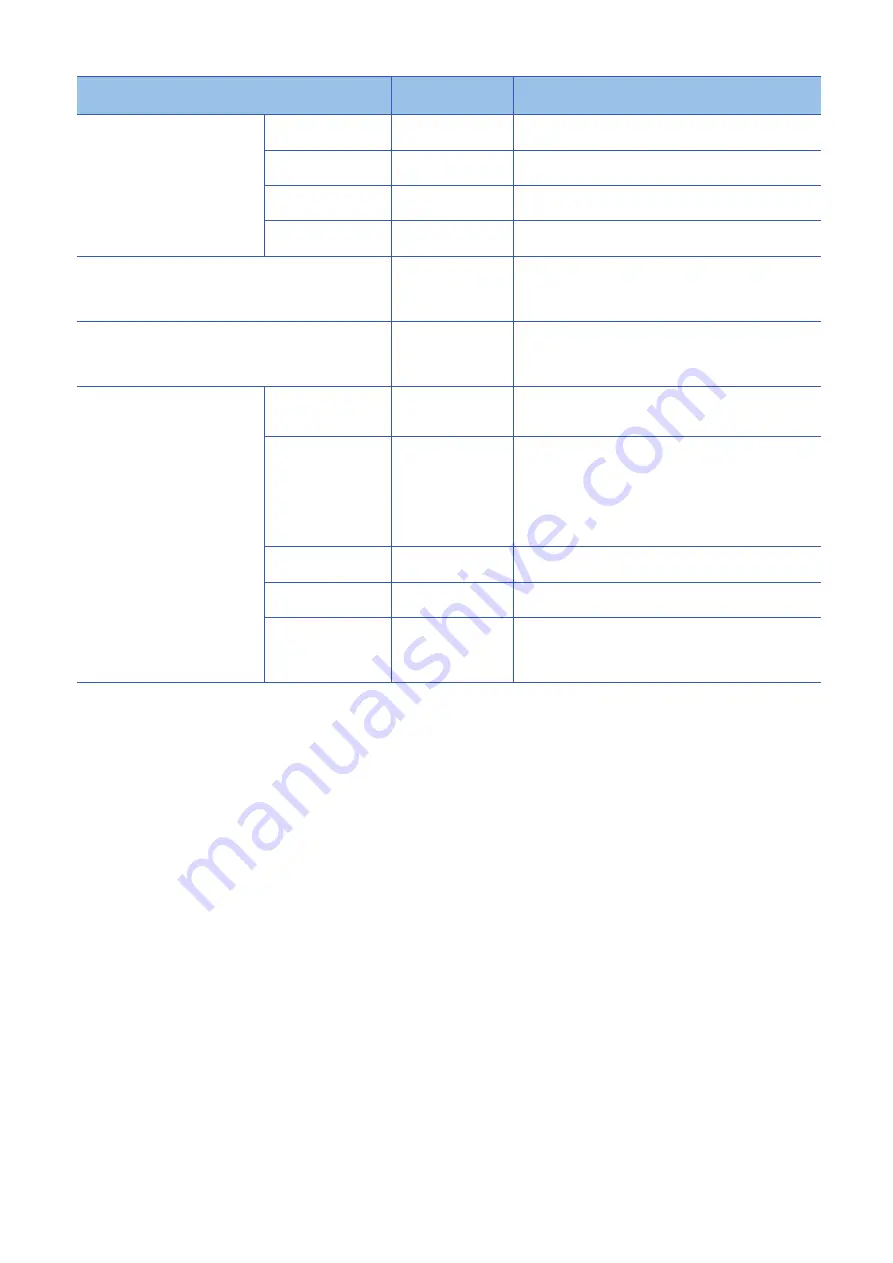
Speed control
1-axis speed control
Forward run speed 1
Reverse run speed 1
Performs the speed control of the specified one axis.
2-axis speed control
Forward run speed 2
Reverse run speed 2
Performs the speed control of the specified two axes.
3-axis speed control
Forward run speed 3
Reverse run speed 3
Performs the speed control of the specified three axes.
4-axis speed control
Forward run speed 4
Reverse run speed 4
Performs the speed control of four axes.
Speed-position switching control
Forward run speed-
position
Reverse run speed-
position
Performs the speed control, and position control (Positioning
with the specified address or movement amount) immediately
after that by turning on Speed-position switching signal.
Position-speed switching control
Forward run position-
speed
Reverse run position-
speed
Performs the position control, and speed control immediately
after that by turning on Position-speed switching signal.
Other controls
NOP instruction
NOP instruction
A control method that is not executed. When the NOP
instruction is set, the operation of the next data starts and this
instruction is not executed.
Current value change
Current value change
Changes the value in [Md.20] Current feed value to the address
set in the positioning data.
The following two methods can be used.
(Machine feed value cannot be changed.)
• Current value change using the control method
• Current value change using the start No. for a current value
change (No.9003)
JUMP instruction
JUMP instruction
Unconditionally or conditionally jumps to the specified
positioning data No.
LOOP
LOOP
Performs the repetition control with the LOOP to LEND
instructions.
LEND
LEND
Returns to the beginning of the repetition control with LOOP to
LEND instructions. When the repetition of the instructions has
been completed for the specified number of times, the operation
of the next positioning data starts.
Major positioning control
[Da.2] Control
method
Description
Summary of Contents for MELSEC iQ-R RD75P4
Page 1: ...MELSEC iQ R Positioning Module User s Manual Application RD75P2 RD75P4 RD75D2 RD75D4 ...
Page 2: ......
Page 13: ...11 MEMO ...
Page 19: ...17 CONTENTS INDEX 588 REVISIONS 592 WARRANTY 593 TRADEMARKS 594 ...
Page 498: ...496 13 PROGRAMMING 13 2 List of Labels Used ...
Page 503: ...13 PROGRAMMING 13 4 Program Example 501 13 ...
Page 514: ...512 13 PROGRAMMING 13 4 Program Example Restart program Parameter data initialization program ...
Page 515: ...13 PROGRAMMING 13 4 Program Example 513 13 Flash ROM write program Error reset program ...
Page 516: ...514 13 PROGRAMMING 13 4 Program Example Stop program ...
Page 565: ...APPENDICES Appendix 4 Operation Examples of When the Remote Head Module Is Mounted 563 A ...
Page 597: ......






























