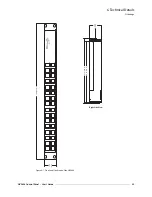
NV9604 Control Panel • User’s Guide
35
7. Misc. Topics
Chapter 7 provides a glossary:
Glossary
AES/EBU
(Audio Engineering Society/European Broadcasting Union). AES and EBU are standards organiza-
tions.
Breakaway
A condition where a destination has multiple sources on different levels.
Category
A category represents a set of devices. (The concept of categories exists to make it easier to select
devices at a control panel.) A category can contain sources, destinations, or devices that are both
sources and destinations. Each device in the category has a unique selection index within that cate-
gory. Each category has a mnemonic ID associated with it.
The NV9604 does not support categories or category selection.
Data Routing
Data routing (a.ka., machine control routing) is a bidirectional form of routing. Routes are charac-
terized by a controlling device and controlled device(s). The NV9604 provides certain data routing
options including a ‘Broadcast’ button.
Device
A “device” is a grouping of input and output ports that define a logical entity. (The logical entity
often represents a real device, but it does not have to be a real entity.) For example, a system might
have 3 levels: video, AES, and time code. A hypothetical device in this system is Camera 1, which
consists of video on input port 1 of the video router, AES on input port 5 of the AES router, and
time code on input port 8 of the time code router.
GPIO
General Purpose Input and Output. A generic term for the NV9604’s tally interface. The tally inter-
face is called the “GPI Interface” at the rear of the NV9604.
Level set
A level set is a group of virtual levels that are commonly used together when switching devices. A
level set also defines the mapping of each virtual level within the level set to a single physical level.
All levels in a level set have a unique display index within that level set.
Multi-Destina-
tion (Mode)
A mode on an NV9000 control panel that presents many destinations at once, in contrast to X-Y
mode. An operator may route sources to multiple destinations in a single take. Multi-destination
mode does not permit the selection of breakaway levels.
Operator
The term operator (a.k.a. user) usually refers to users other than the system administrator or config-
urer. An operator is responsible for making the routes.
Physical Level
Multiple routers provide different “physical levels” on which to switch the signals of devices. Any
particular device might send or receive HD, SD, AES, time-code, or machine-code signals.
PIN
The system administrator may create a single “super user” personal identification number (PIN)
that functions as a passcode. A PIN is 4–6 digits in length. The PIN allows certain operators to per-
form functions such as (1) forced release on a control panel that is configured for normal release or
(2) changing the ID of a control panel.