Older keyboards, and especially those used in old analog organs, usually don't have
such a thing, so in order to use 8x8 scanner, you must build diode matrix yourself,
assuming it is possible to separate the contacts into groups of 8 keys. In other
cases, when making diode matrix is impractical, you may use bus-bar type of
scanners (BBS), where all keys share only one common bus. This is typical
keyboard arrangement in all old organ consoles. Below is a short table showing
which scanner type can be used with different keyboards:
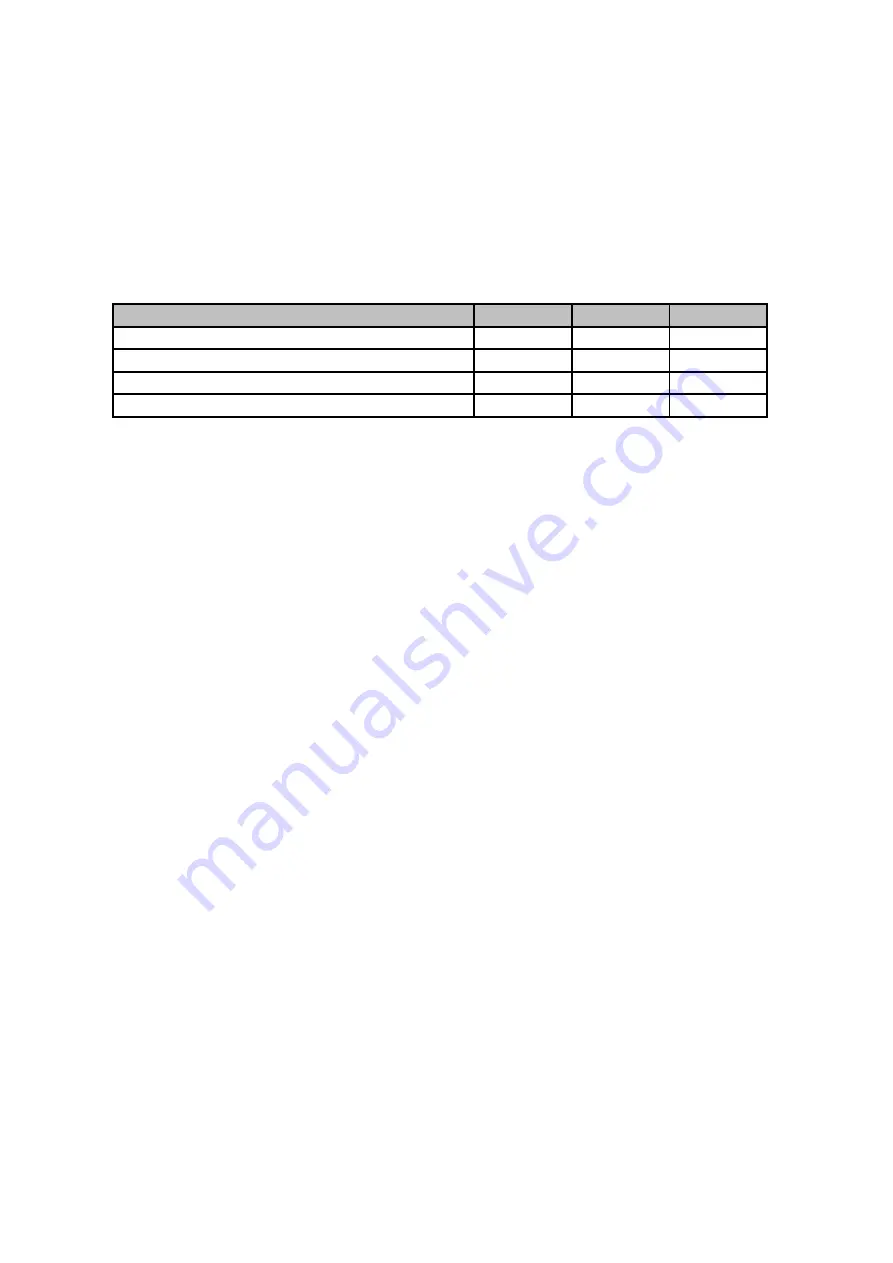
Keyboard type
DMS
BBS
PDS
Independent switches, no connections
◊
●
◊
Switches organized in 8x8 diode matrix
●
‡
●
Switches organized in 6x12 and other
‡
One common rail for all switches
‡◊
●
‡◊
● - can be used directly
◊ - with additional diodes
‡ - requires rewiring of existing contacts.
3.1
Split for special function inputs - #905
By default all 63 on-board inputs are treated as keyboard interface, playing notes,
or other similar MIDI events as described in chapter 5. But you can designate a few
inputs for other tasks if less keyboard inputs are required. Such altered inputs work
like they would be potentiometer inputs, but only with min and max values (0 and
127) possible. If those buttons are assigned this way, each of them can be
individually set to different event type and MIDI channel. It creates some new
possibilities - for example you can assign transpose//- buttons, channel
+/- buttons, and a few non-continuous CCs, with most obvious examples like
Sustain or Portamento.
There can be up to 15 such inputs, and they are always placed at the top of note
contacts, in the last, 4th connector (J4) of MBBS. This special mode is available
only in MBBS and not in any of connected scanners.
To define the split point between normal note inputs, and special CC inputs, play
any note at MBBS on-board inputs, enter command #905 from the keypad (or use
on-board inputs in sequence: 64, 10, 1, 6), and then press the top key of desired
note part. All inputs above this point, up to the EDIT input, will be now acting like
inputs of POT scanner and can be individually programmed. To cancel this setting,
and turn the whole range as normal inputs, repeat the procedure, but now set the
split point at the last note input (63). Do NOT connect any potentiometer, or
variable voltage to those inputs. They are only capable of working with switches, or
logic levels. Applying other voltages may damage the board.
This kind of split has nothing to do with keyboard split described in chapter 5.5 and
can be used independently of that one.
6





















