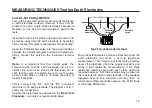
The instrument uses the four terminal method of
measurement. A reversing d.c. test current is injected
into the earth through terminals ‘C1’ and ‘C2’. The
potential developed across the earth is monitored with
‘P1’ and ‘P2’. A three pole test is achieved by shorting
terminals ‘C1’ and ‘P1’ together through an internal
relay.
At the beginning of a test, the control logic initiates a
Potential spike resistance check, monitoring the input
over-range detector for the result. The instrument
autoranges by the control logic monitoring the output of
the over-range detector and switching the current
source to a lower current output. The instrument also
autoranges if the high current loop resistance detector
senses too much current loop resistance for the preset
range.
The instrument measuring circuitry is connected to
terminals ‘P1’ and ‘P2’. The voltage limiter and input
buffer prevent damage to the instrument and loading of
the resistance under test. Synchronous filtering and
detection are used to recover the test signal from noisy
environments followed by filtering and conversion to a
reading by the digital panel meter.
The test signal frequency is produced by dividing the
frequency of a crystal oscillator. This is then passed
through logic circuitry to produce the waveforms for
synchronous filtering and detection.
29
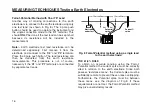
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
High Current
loop resistance
detector
Filtering
and
detection
Digital
panel
meter
Crystal
oscillator
Switcheable
current
source
Frequency
divider and
waveform
generator
Control logic
Input overload
comparator
Potential spike
resistance test
Over-range
detector
Input buffer
and voltage
limiter
C1
P2
P1
C2
0V
3 pole test
Fig. 21 Block diagram of instrument circuit
Summary of Contents for DET5/4D
Page 41: ...41...