Information Manual
DSP1611/17/18/27/28/29 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
April 1998
Serial I/O
Lucent Technologies Inc.
DRAFT COPY
7-17
7.6 Multiprocessor Mode Description
(continued)
7.6.2 Detailed Multiprocessor Mode Description
Three registers associated with multiprocessor mode are the time-division multiplexed slot (tdms) register (see
), the serial receive and transmit address (srta) register (see
), and the serial input address
(saddx) register. Multiprocessor mode requires no external logic and uses a TDM interface with eight time slots
per frame. A serial address on the SADD line is sent simultaneously with data on DO from any one device in a pre-
determined time slot, and the data is received only by other device(s) having the address specified. Each device
has both a user-programmable receive address and transmit address associated with it.
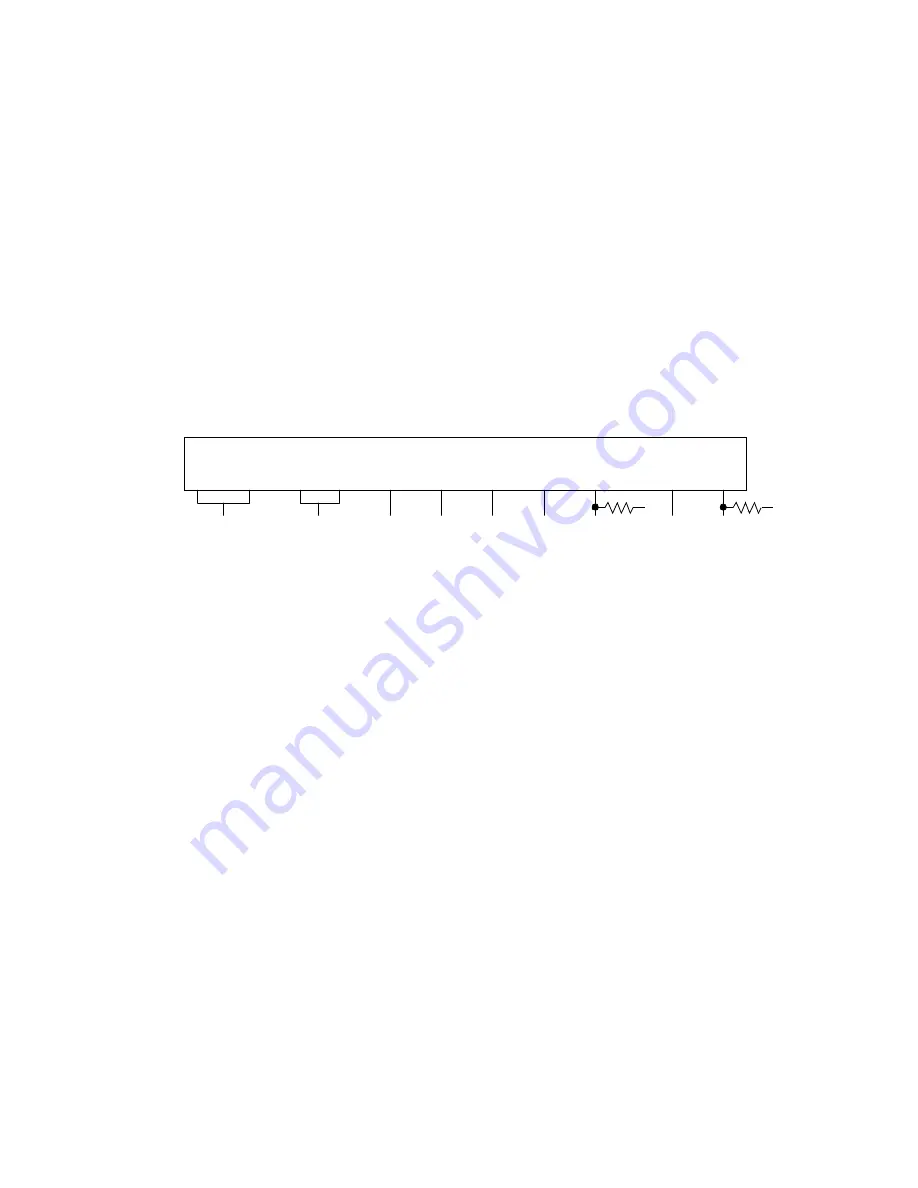
In multiprocessor mode, the following pins are connected together to form a four-wire bus as shown in
.
The DI and DO pins form a single-wire data bus referred to as DATA. ICK and OCK form a clock line referred to as
CK. SADD forms a single-wire address bus referred to as ADD. And, SYNC provides a synchronization line
referred to as SYN. Typically, one particular device is specified statically to always drive CK and SYN, although CK
can also be generated by an external clock. The signals are generated by the DSP device having active SYNC and
OCK signals that occur if the tdms register SYNC field is set and the sioc register OCK field is set.
5-4184
Figure 7-14. DSP1611/17/18/27/28/29 Multiprocessor Connections
The other devices use the SYNC and OCK signals in the passive mode to synchronize operations. All DSPs must
have their ILD and OLD signals in active mode. Although these signals are not required externally for the operation
of multiprocessor mode, they are used internally in the SIO and must be active for that reason.
DO
ICK
OCK
ILD
OLD
IBF
OBE
SADD
SYNC
DOEN
DATA
CK
NC
NC
NC
NC
ADD
SYN
DSP1611/17/18/27/28/29
NC
V
DD
V
DD
DI
Summary of Contents for DSP1611
Page 18: ...Chapter 1 Introduction...
Page 27: ...Chapter 2 Hardware Architecture...
Page 52: ...Chapter 3 Software Architecture...
Page 116: ...Chapter 4 Instruction Set...
Page 154: ...Chapter 5 Core Architecture...
Page 176: ...Chapter 6 External Memory Interface...
Page 208: ...Chapter 7 Serial I O...
Page 237: ...Chapter 8 Parallel I O DSP1617 Only...
Page 261: ...Chapter 9 Parallel Host Interface PHIF DSP1611 18 27 28 29 Only...
Page 275: ...Chapter 10 Bit I O Unit...
Page 284: ...Chapter 11 JTAG Test Access Port...
Page 306: ...Chapter 12 Timer...
Page 313: ...Chapter 13 Bit Manipulation Unit...
Page 325: ...Chapter 14 Error Correction Coprocessor DSP1618 28 Only...
Page 350: ...Chapter 15 Interface Guide...
Page 367: ...Appendix A Instruction Encoding...
Page 379: ...Appendix B Instruction Set Summary...
Page 381: ...aD extractz aS IM16 B 52 aD insert aS arM B 53 aD insert aS IM16 B 54 aD aS aaT B 55...
Page 437: ...Index...















































