323
Learning Protection Features
Note
Overload warnings warn of an overload before an overload fault trip occurs. The overload
warning signal may not work in an overload fault trip situation, if the overload warning level (OL
Warn Level) and the overload warning time (OL Warn Time) are set higher than the overload trip
level (OL Trip Level) and the overload trip time (OL Trip Time).
6.1.4 Stall Prevention and Flux Braking
The stall prevention function is a protective function that prevents motors from stalling due
to overloads. If a motor stall occurs due to an overload, the inverter operation frequency is
adjusted automatically. When a stall is caused by overload, high currents induced in the
motor may cause motor overheating or damage the motor and interrupt operation of the
motor-driven devices.
In this case, the motor decelerates with optimum deceleration without a braking resistor by
using flux braking. If the deceleration time is too short, an over voltage fault trip may occur
because of regenerative energy from the motor. The flux braking makes the motor use
regenerate energy, therefore optimum deceleration is available without over voltage fault
trip.
To protect the motor from overload faults, the inverter output frequency is adjusted
automatically, based on the size of load.
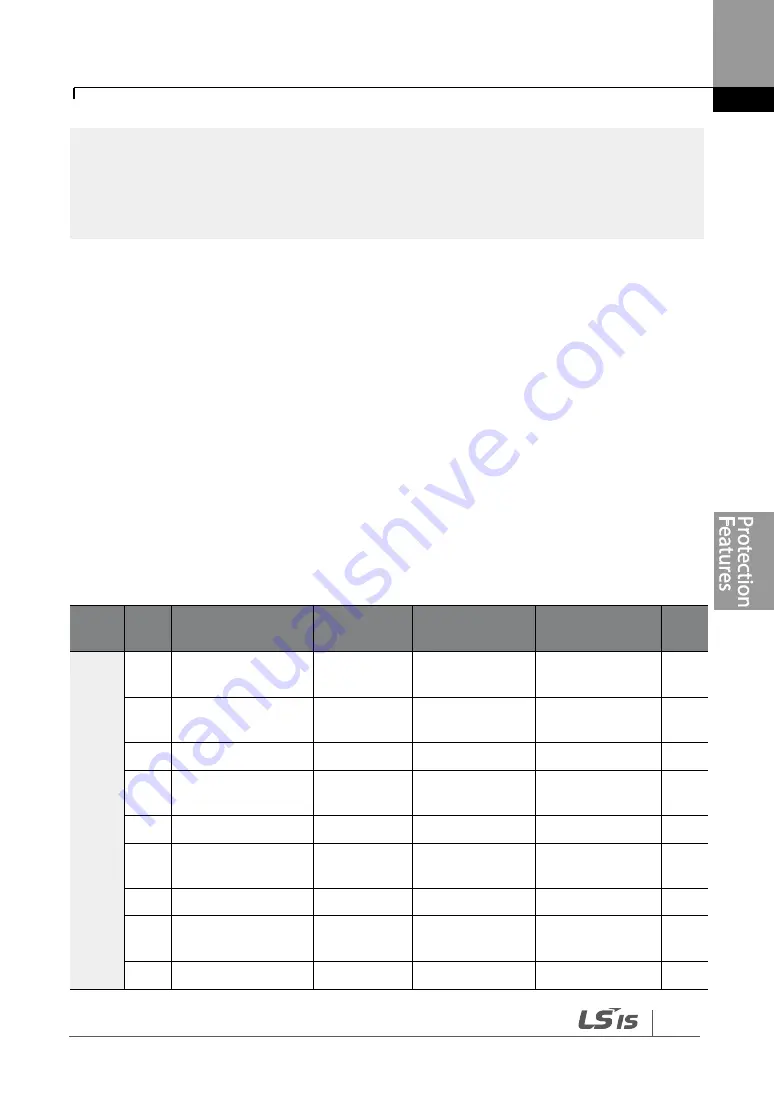
Group Code Name
LCD Display
Parameter
Setting
Setting range
Unit
PRT
50
Stall prevention
and flux braking
Stall Prevent 0100
-
bit
51
Stall frequency 1
Stall Freq 1
60.00
Start Freq
–Stall
Freq 1
Hz
52
Stall level 1
Stall Level 1 130
30
–150
%
53
Stall frequency 2
Stall Freq 2
60.00
Stall Freq 1
–Stall
Freq 3
Hz
54
Stall level 2
Stall Level 2 130
30
–150
%
55
Stall frequency 3
Stall Freq 3
60.00
Stall Freq 2
–Stall
Freq 4
Hz
56
Stall level 3
Stall Level 3 130
30
–150
%
57
Stall frequency 4
Stall Freq 4
60.00
Stall Freq 3
–
Maximum Freq
Hz
58
Stall level 4
Stall Level 4 130
30
–150
%
Summary of Contents for H100
Page 14: ......
Page 18: ...Preparing the Installation 4 37 90 kW 3 Phase ...
Page 27: ...Preparing the Installation 13 ...
Page 47: ...33 Installing the Inverter ...
Page 48: ...Installing the Inverter 34 Input and Output Control Terminal Block Wiring Diagram ...
Page 61: ...47 Installing the Inverter ...
Page 71: ...Learning to Perform Basic Operations 57 ...
Page 88: ...Learning to Perform Basic Operations 74 ...
Page 103: ...89 Learning Basic Features Code Description V1 Quantizing ...
Page 129: ...115 Learning Basic Features ...
Page 140: ...Learning Basic Features 126 ...
Page 148: ...Learning Basic Features 134 ...
Page 171: ...157 Learning Advanced Features Deceleration dwell operation ...
Page 183: ...169 Learning Advanced Features ...
Page 184: ...Learning Advanced Features 170 PID Command Block ...
Page 185: ...171 Learning Advanced Features PID Feedback Block ...
Page 186: ...Learning Advanced Features 172 PID Output Block ...
Page 187: ...173 Learning Advanced Features PID Output Mode Block ...
Page 197: ...183 Learning Advanced Features ...
Page 201: ...187 Learning Advanced Features Code Description 100 EPID1 Control block ...
Page 202: ...Learning Advanced Features 188 EPID2 Control block ...
Page 237: ...223 Learning Advanced Features Time Period Schedule AP3 38 Except3 Day 01 01 ...
Page 244: ...Learning Advanced Features 230 ...
Page 259: ...245 Learning Advanced Features Code Description Code Description Volt ...
Page 362: ...Learning Protection Features 348 ...
Page 415: ...401 RS 485 Communication Features Item Standards Parity check None ...
Page 524: ...Table of Functions 510 ...
Page 533: ...Table of Functions 519 ...
Page 547: ...533 Troubleshooting ...
Page 585: ...Technical Specification 571 ...
Page 594: ...580 ...
Page 595: ...581 ...
Page 596: ...582 ...