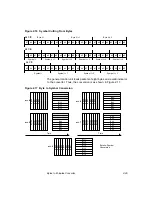
Square Root Nyquist Filter
2-29
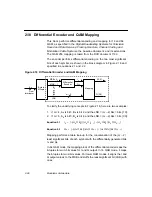
Figure 2.20 Output Scaling by Arithmetic Shift Right
The shifter treats the value of BITS_TO_SHIFT[3:0] like a coefficient, and
the value is available separately for every phase. This means that the
hardware of the filter is multiplexed in such a way that there are the same
coefficient registers for the I and Q channel, and each of the two MACs
switches between four banks of coefficients cyclically, driven by OCLK.
Setting all coefficients to zero (except the center coefficient, which is 1),
offers a bypass mode for the filter.
The interpolator following the Nyquist filter receives 12-bit resolution in
PLL Mode 2. Program the shifter accordingly to make the increase
precision available to the interpolator; for example: to 3 rather than 5.
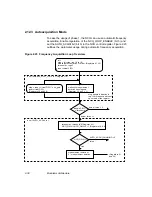
2.11.1 Filter Setup Procedure
The filter module is loaded with 31 filter coefficients sequentially, with four
blocks of 49 bytes in the PHASE_0, PHASE_1, PHASE_2, and
PHASE_3 registers (Register 0 of Group 2). The same data controls the
I and Q data path in parallel. Also, the filter is loaded with four
BITS_TO_SHIFT and an 11-bit offset value for each phase. It is specified
within 49 bytes in each phase, as shown in Table 2.1. The complete
setup sequence consists of 4 * 49 = 196 bytes for all four phases. The
filter organizes the coefficient registers for each register bank as
described below, using the coefficient enumeration shown in the block
diagram. Note that no meaningful operation can be performed while the
filter is being programmed, since the old coefficients are being shifted out
while the new ones are programmed in.
Shifter
I[9:0]
Shifter
Q[9:0]
BITS_TO_SHIFT[3:0]
IS[19:0]
QS[19:0]
Summary of Contents for L64777
Page 1: ...L64777 DVB QAM Modulator Order Number I14031 A Technical Manual June 2000...
Page 10: ...x Contents...
Page 14: ...1 4 Introduction...
Page 90: ...5 10 Signals...
Page 110: ...A 8 Programming the L64777 in Serial Host Interface Mode...
Page 116: ...C 2 Monitoring Device Internal Signals...
Page 124: ......