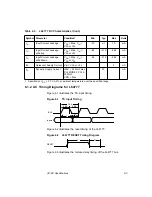
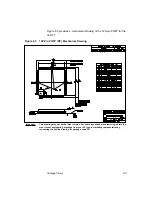
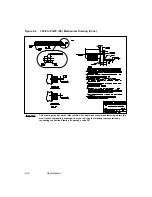
Read Cycle Using the Serial Bus Interface
A-5
7.
The master generates another start condition.
8.
The master repeats steps 2–7 to address the appropriate group and
write 1 or more data bytes.
9.
The master terminates the cycle by issuing a stop condition.
Figure A.4
Burst Write to Slave (Master-Transmitter, Slave-Receiver)
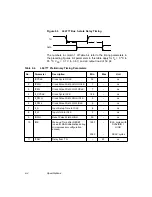
A.4 Read Cycle Using the Serial Bus Interface
Figure A.5 shows the timing for a burst, or a single read cycle. The
following cycles must take place for a read cycle:
1.
The master starts the cycle by issuing a start condition.
2.
The master transmits the 7-bit slave address.
3.
The master sets the R/W bit = 0 to indicate a write cycle.
4.
The addressed slave acknowledges the reception of the slave
address by driving SDA low in the ACK cycle.
5.
The master sends the 8-bit Group 0 address (0x0) to indicate that
the APR is to be loaded. (The master accesses Group 0 only to load
the APR.)
Start
Stop
SCL
SDA
Condition
Condition
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
R/W
ACK
(Slave)
Bit 0
7-bit Slave
Address
8-bit Group
ACK
(Slave)
2
3
1
ACK
(Slave)
Address
8-bit Data
Start
Condition
7
4
5
6
7-bit Slave
Address
ACK
(Slave)
ACK
(Slave)
ACK
(Slave)
ACK
(Slave)
8-bit Group
Address
8-bit Data
8-bit Data
9
8
SDA
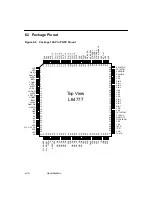
Summary of Contents for L64777
Page 1: ...L64777 DVB QAM Modulator Order Number I14031 A Technical Manual June 2000...
Page 10: ...x Contents...
Page 14: ...1 4 Introduction...
Page 90: ...5 10 Signals...
Page 110: ...A 8 Programming the L64777 in Serial Host Interface Mode...
Page 116: ...C 2 Monitoring Device Internal Signals...
Page 124: ......