4.3.4
MIG Torch
Liner Types
and
Information
MIG Torch Liners
The liner is both one of the simplest and most important components of a MIG gun. Its sole purpose is
to guide the welding wire from the wire feeder, through the gun cable and up to the contact tip.
Steel Liners
Most MIG gun liners are made from coiled steel wire also known as piano wire, which provides the
liner with good rigidity and flexibility and allows it to guide the welding wire smoothly through the
welding cable as it bends and flex during operational use. Steel liners are primarily used for feeding
of solid steel wires, other wires such as Aluminium, Silicon Bronze etc will perform better using a teflon
or Polyamide line. The internal diameter of the liner is important and releative to the wire diameter
being used and will assit in smooth feeding and prevention of the wire kinking and birdnesting at the
drive rollers. Also bending the cable too tightly during welding increases the friction between the
liner and the welding wire making it more difficult to push the wire through the liner resulting in poor
wire feeding, prematureliner wear and birdnesting. Dust, grime and metal particles can accumalate
inside the liner over time and cause friction and blockages, it is recommended to periodically blow
out the liner with compressed air. Small diameter welding wires, 0.6mm through 1.0mm have
relatively low columnar strength, and if matched with an oversized liner, can cause the wire to
wander or drift within the liner. This in turn leads to poor wire feeding and premature liner failure due
to excessive wear. By contrast, larger diameter welding wires, 1.2mm through 2.4mm have much
higher columnar strength but it is important to make sure the liner has enough internal diameter
clearance. Most manufacturers will produce liners sized to match wire diameters and length of
welding torch cable and most are colour coded to suit.
4.3.5
MIG
Welding
Definition of MIG Welding
MIG (metal inert gas) welding also known as GMAW (gas metal arc welding) or MAG (metal active
gas welding), is a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process in which a continuous and
consumable wire electrode and a shielding gas are fed through a welding gun. A constant voltage,
direct current power source is most commonly used with MIG welding. There are four primary
methods of metal transfer in MIG welding, called short circuit (also known as dip transfer) globular
transfer, spray transfer and pulsed-spray, each of which has distinct properties and corresponding
advantages and limitations. To perform MIG welding, the basic necessary equipment is a welding
gun, a wire feed unit, a welding power supply, an electrode wire, and a shielding gas supply. Short
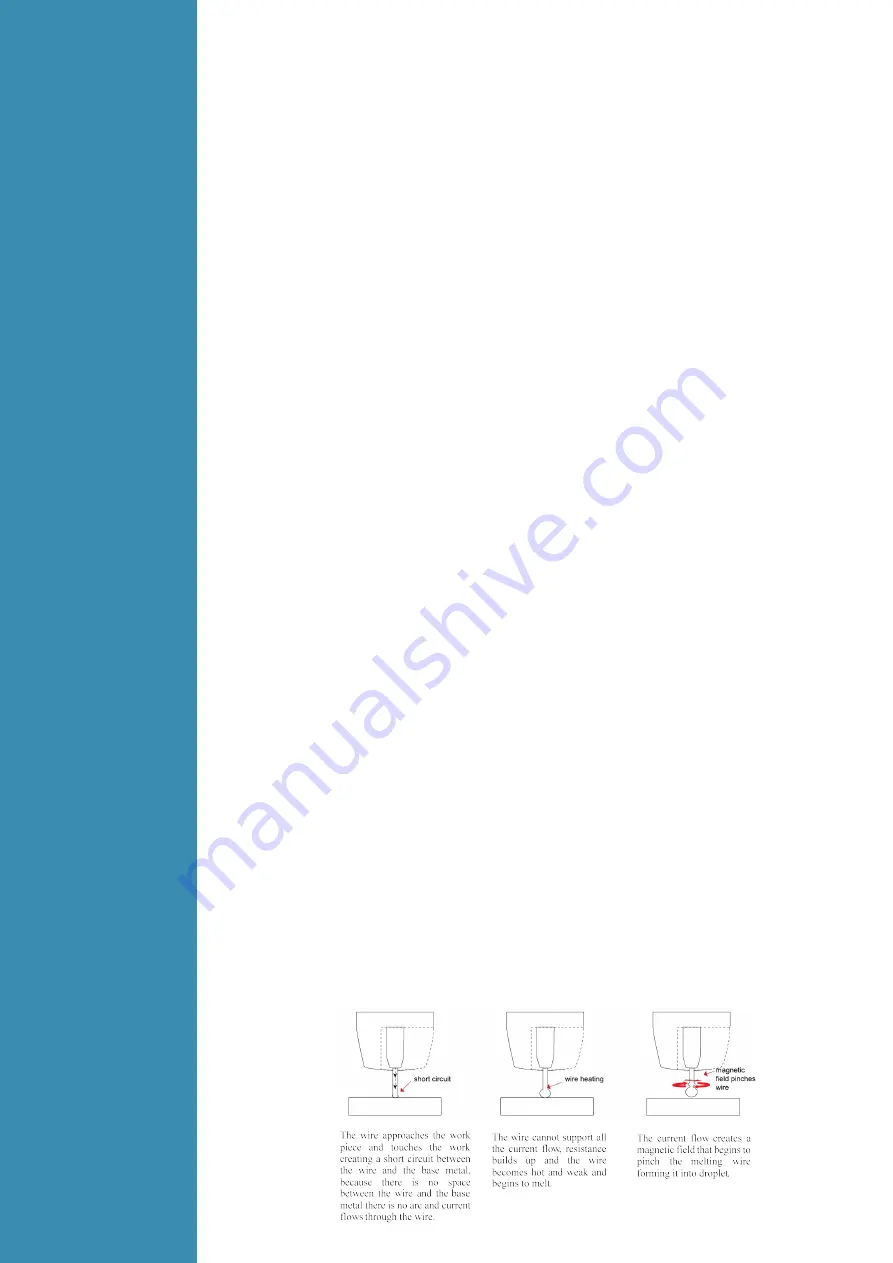
circuit transfer is the most common used method whereby the wire electrode is fed continuously
down the welding torch through to and exiting the contact tip. The wire touches the work piece and
causes a short circuit the wire heats up and begins to form a molten bead, the bead separates from
the end of the wire and forms a droplet that is transferred into the weld pool. This process is repeated
about 100 times per second, making the arc appear constant to the human eye.
Short Circuit Transfer
- Short circuit transfer is the most common used method whereby the wire
electrode is fed continuously down the welding torch through to and exiting the contact tip. The wire
touches the work piece and causes a short circuit the wire heats up and begins to form a molten
bead, the bead separates from the end of the wire and forms a droplet that is transferred into the
weld pool. This process is repeated about 100 times per second, making the arc appear constant
to the human eye.
Basic MIG Welding




















