19
BOC Smootharc TIG 200 DC Operating Manual
3.5 Copper and copper alloys
Cleanliness is important when welding copper, and all dirt, grease, and
other contaminants must be removed before welding. Copper alloys
containing aluminium will form a surface oxide film and this must also be
removed before welding. Preheat will be required for unalloyed copper
but some copper alloys can be TIG welded without preheat except on
thick sections.
Standard DC TIG welding equipment is suitable for most copper and
copper alloys, but aluminium bronze is normally TIG welded using AC
current to break down the tenacious oxide film on the surface.
Pure argon, helium, or argon-helium mixtures are standard shielding
gases for DC TIG welding copper and copper alloys. Alushield Heavy
is ideal for TIG welding copper and some copper alloys, particularly in
thicker sections. Pure argon is the shielding gas used for AC TIG welding.
TIG consumables are solid filler rods based on pure copper and several
copper alloy compositions, including aluminium bronzes, silicon bronzes,
and cupro-nickels. It is normal to try to use a filler material with a similar
composition to that of the parent material but this is not always possible,
and sometimes not desirable.
Porosity is the main welding problem encountered when TIG welding
unalloyed copper and some copper alloys are prone to solidification
cracking and porosity. Certain alloys are difficult to weld (brass will lose
zinc if welding is attempted), and welding is not recommeded for those
containing lead.
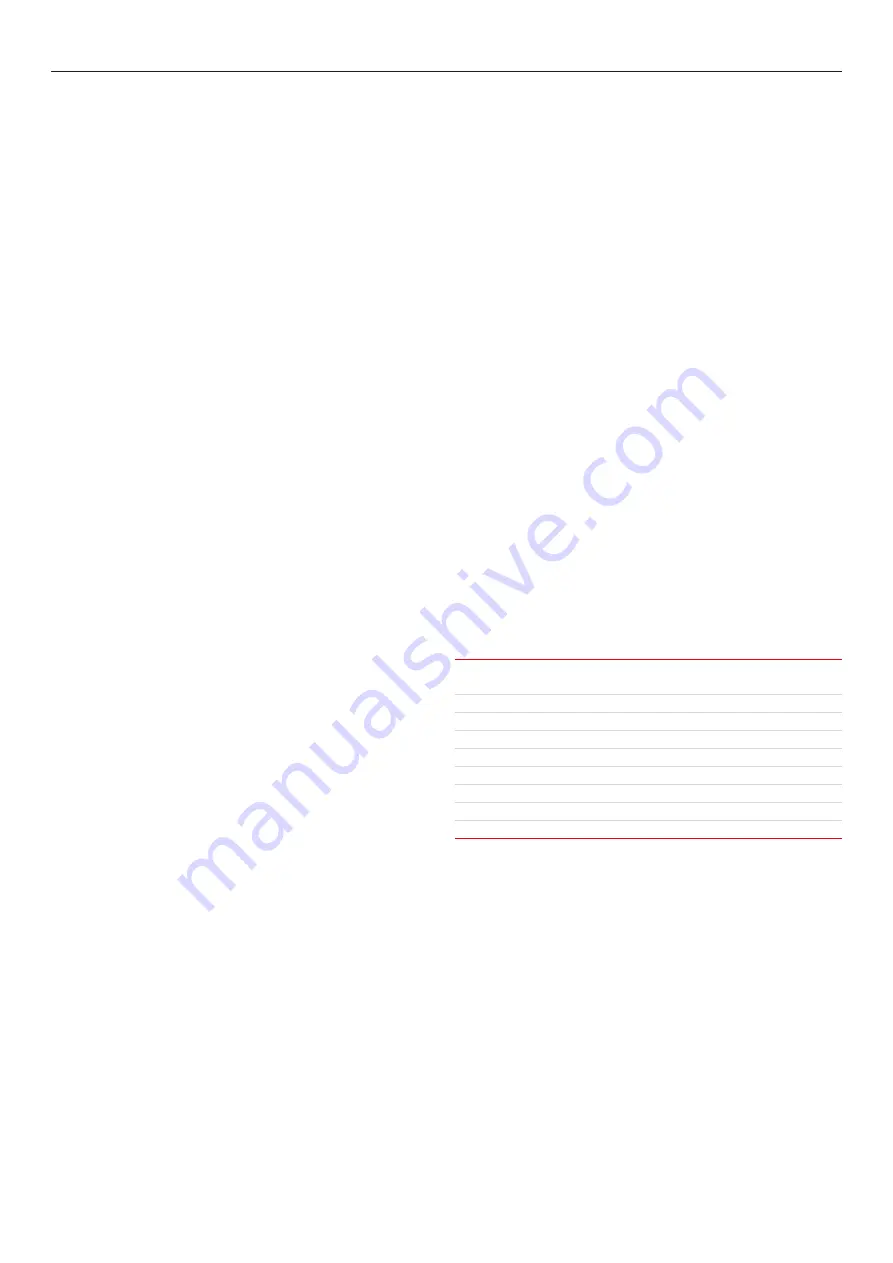
Copper and copper alloy welding parameters
Plate thickness (mm)
1.5
3
5
Joint type
Square butt Square butt Square butt
Root gap (mm)
1.0
2.0
3.0
Layers
1
1
2
Tungsten size (mm)
1.6
3.2
4.0
Consumable size (mm)
2.0
3.2
4.0
Current (A)
120
185
270
Welding speed (cm/min)
0.29
0.25
0.15
Gasflow (l/min)
7
8
8






























