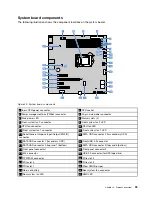
The ThinkServer EasyStartup program main interface provides the following menus on the left pane of
the screen.
Menu item
Description
Home
Provide general information about the program.
Compatibility notes
Provide information about the operating systems and server
configurations supported by the version of the program you are using.
User Guide
Provide information about the features of the program and instructions
on how to use the program.
Hardware list
Display a list of hardware devices detected by the program.
Configure RAID
Instruct you to configure RAID or view the current RAID configuration
and make changes if needed.
Install operating system
Display a series of choices and prompts to collect information
required for operating system installation, prepare the hard disk drive
for installation, and then initiate the installation process using your
operating system installation disc.
Driver download
Provide the supported device drivers for download.
About
Provide the version information and legal notices.
Configuring RAID
This topic provides information about RAID and the utility programs that are available for you to configure
RAID.
This topic contains the following items:
•
•
“RAID for your server” on page 49
•
“Configuring onboard SATA software RAID” on page 50
•
“Configuring advanced SATA or SAS hardware RAID” on page 52
About RAID
RAID, an acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a technology that provides increased
storage functions and reliability through redundancy. This is achieved by combining multiple HDDs into a
logical unit, where data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways called RAID levels.
When a group of independent physical HDDs are set up to use RAID technology, they are in a RAID array.
This array distributes data across multiple HDDs, but the array appears to the host server as one single
storage unit. Creating and using RAID arrays provides high performance, such as the expedited I/O
performance, because several drives can be accessed simultaneously.
RAID drive groups also improve data storage reliability and fault tolerance compared with single-drive
storage systems. Data loss resulting from a drive failure can be prevented by reconstructing missing data
from the remaining drives.
The following list describes some of the most commonly used RAID levels:
.
47
Summary of Contents for ThinkServer TS460
Page 14: ...xii ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 18: ...4 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 52: ...38 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 68: ...54 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 138: ...124 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 144: ...130 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 148: ...134 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 160: ...146 ThinkServer TS460 User Guide and Hardware Maintenance Manual ...
Page 171: ......
Page 172: ......