IM-T-221B May,2018
DTC-A Clip-type Displacement Transducer INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Thank you for purchasing this KYOWA product. Before using it,
read this instruction manual carefully. Also, keep the manual within
easy reach so that you can refer to it whenever necessary.
1.
Calling the operator’s attention
Be sure to observe the accompanying precautions preserve the
performance of the instrument.
Caution
It is a precaution to operate properly.
2.
Handling precautions
Caution
Do not expand the space between the two beams or narrow it
even after they get in touch with the stoppers.
This product is exclusively designed for indoor use. When using
it, take care to avoid the direct rays of the sun, water, oil and
solvent.
Avoid measurement under vibration or impact.
Do not disassemble the displacement transducer.
3.
Installation
The mounting sections of the transducer (the respective heads of
the two beams) are so designed that they confirm with the ASTM
(American Society for Testing & Materials) Standards E399. Use
the transducer properly by referring to the standards.
3.1
How to mount
On the measuring area, prepare two opposed grooves to
accept the transducer, or mount the transducer by screwing or
bonding two opposed tips (TIP-10A) (available as options) to
the transducer mounting section.(See Fig.3.1.1 and 3.1.2)
Fig.3.1.1 Configuration of groove on measuring object (ASTM Std.)
Fig.3.1.2 Configuration of tip (TIP-10A) (option)
When the two beams are free, the space between them is about
11mm. The measuring range is denoted by the space between the
mounting grooves. It is 4 to 9mm on DTC-A-5 and 8 to 10mm on
DTC-A-2. Fix the cable nearby the mainframe so that the mass of
the cable will not affect the transducer.
4.
Connection and measurement
4.1
Connect the transducer to a strain amplifier.
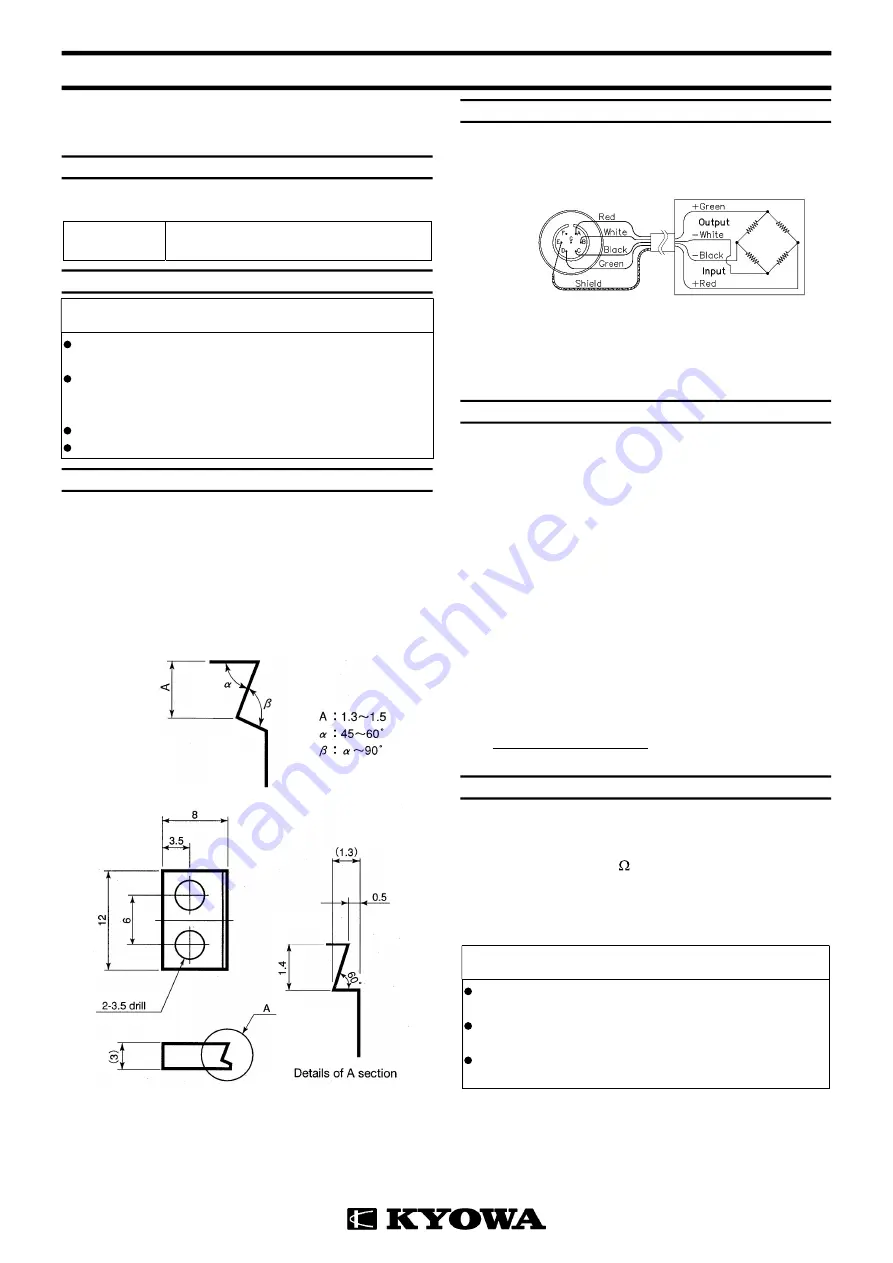
4.2
Perform connection as illustrated below when using an NDIS
connector.
Displacement transducer
(The shield wire is not connected to the mainframe.)
4.3
It is required to heat-run for 5 to 10 minutes before starting the
measurement.
4.4
Measurement values increase in the PLUS direction as space
grows between the beams.
5.
Conversion
5.1
Use the calibration constant described in the test data sheet to
convent a reading into a displacement value.
5.2
When a strain amplifier is in use, output reads in μm/m
equivalent strain (×10
-6
equivalent strain). Find a displacement
value corresponding to μm/m. Then, obtain a displacement
value through multiplication using the following equation.
Displacement value(mm)
=Strain amplifier's output (μm/m)
×Calibration constant (mm/1μm/m)
5.3
When using an amplifier of other type or a recorder, first find
the exact bridge exciting voltage applied. Second, find the
displacement value that corresponds to 1(μV) output voltage
against 1(V) bridge excitation voltage. Then, obtain the
displacement value through multiplication using the following
equation.
Displacement value(mm)
=
Bridge output voltage(μV)
×Calibration constant (mm/1μV/V)
Bridge excitation voltage(V)
6.
Storage and inspection
6.1
Avoid water, oil and dust on the displacement transducer.
6.2
If an abnormal initial value or reading appears, measure input
resistance, output resistance as well as insulation resistance
(which should be 100M or higher) between the main body
and red to green.
If abnormal resistance is found, the cause may be failure of the
sensing element. In this case, contact your KYOWA
representative for necessary inspection.
Caution
To measure insulation resistance, apply a voltage lower than
50V to the insulation resistance tester.
When storing the transducer, be sure that it is free from
displacement.
Avoid storing the transducer where it is exposed to especially
high or low temperature or much dust.






















