Section 4: Measure considerations
Model DMM7510 7½ Digit Graphical Sampling Multimeter Reference Manual
4-4
DMM7510-901-01 Rev. B / May 2015
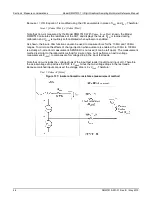
Constant-current source method
For the 1
Ω
to 1 M
Ω
ranges, the Model DMM7510 uses the constant-current method to measure
resistance. This method sources a constant current (I
SOUR
) to the device under test (DUT) and
measures the voltage (V
MEAS
). Resistance (R
DUT
) is then calculated and displayed using the known
current and measured voltage.
Simple schematics of the 2-wire and 4-wire constant-current methods are shown below. The test
current sourced to the DUT depends on the selected measurement range. For example, for the 100
Ω
range, the test current is 1 mA. Because the voltmeter of the Model DMM7510 has high input
impedance (>10 G
Ω
), virtually all the test current (1 mA) flows through the DUT. For a DUT that is
≤
1 k
Ω
, 4-wire ohm measurements should be used as shown. Because the voltage is measured at the
DUT, voltage drop in the test leads is eliminated (this voltage could be significant when measuring a
low-ohm DUT).
Figure 135: Constant-current resistance measurement method