4
www.jetgroupbrands.com
Operating Instructions
1. Check Coolant: Low coolant level causes
foaming and high blade temperatures. Dirty or
weak coolant can clog pump, causes crooked
cuts, low cutting rate and permanent blade
failure. Dirty coolant causes the growth of
bacteria with ensuing skin irritation. Coolant is
water soluble.
2. Keep vise slides clean and oiled.
3. Clean chips from blade wheels and the areas
around wheels. Keep chip brush in good repair.
4. Saw Guide: Keep saw guides properly adjusted.
Loose guides will affect cutting accuracy.
5. Check saw blade for sharpness.
6. Blade Speed: Is blade speed set correctly for
workpiece material and shape?
7. Check Blade Tension: Particularly after initial
cuts with a new blade.
Blade Selection
A. Never use a blade so coarse that less than 3
teeth are engaged in the workpiece at any time.
(Too few teeth will cause teeth to strip out.)
B. Never use a blade finer than required to obtain a
satisfactory surface finish or satisfactory flatness.
(Too many teeth engaged in the work piece will
reduce sawing rate; cause premature blade wear;
produce “dished” cuts or cuts which are neither
square nor parallel.)
C. The chart which follows is intended as a general
guide to good sawing practices. Consult
your blade supplier or qualified technician for
complete information for operational details of
saw blades and their use.
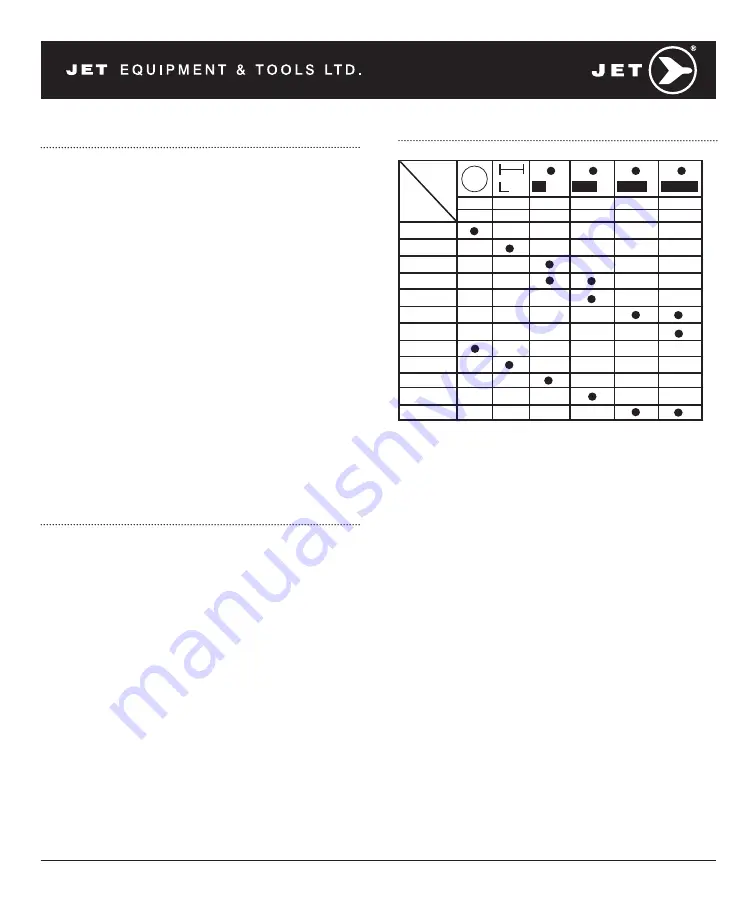
The Selection of Saw Blades
Remarks:
HSS-High Speed Steel Sawblade
HCS-High Carbon Steel Sawblade
NOTE:
1. When standard wall pipe, tubes, channel iron
and angle I beams are cut, a 10 pitch saw blade
of wave-set type or sawblade of (HSS) 6/10T is
frequently used to good advantage.
2. Tubes or materials with wall thickness or web
thickness of 1/2" or more can usually use an 8 or
6 pitch sawblade of (HSS) 4/6T satisfactorily.
3. When rectangular solid bar stock is to be sawed,
the work should be loaded so that the cut is
made across the thinnest cross section. The
pitch (or number of teeth per inch of blade)
selected must provide engagement of at least 3
teeth in the workpiece. Should application of this
rule not be possible because the thinnest cross
section is too thin, the piece must be loaded so
that the cut is made across the wider dimension
and a coarser blade selected from the listing of
recommendations for round and square
solid bars.
Cutting
Material
<3mm >5mm >50mm >100mm >150mm >200mm
Sawblade
<0.12"
>0.2"
>2" >4" >6" >8"
(HSS)
14T
(HSS)
6/10T
(HSS)
5/8T
(HSS)
4/6T
(HSS)
3/4T
(HSS)
2/3T
(HSS)
1/2T
(HCS)
10T
(HCS)
8T
(HCS)
6T
(HCS)
4T
(HCS)
2T
Summary of Contents for JHBS916
Page 5: ...5 www jetgroupbrands com ...
Page 15: ...15 www jetgroupbrands com ...
Page 16: ...16 www jetgroupbrands com ...


































