EMI and Mechanical Design Considerations
152
Design Guide
Differential clocking can also reduce the amount of noise coupled to other traces, which improves
signal quality and reduces EMI. I/O signals are particularly important because they often leave the
system chassis (serial and parallel ports, keyboards, mouse, etc.), and radiate noise that has been
induced onto them. A single-ended clock's return path is usually a reference plane, which is shared
by other signals/traces. When noise is created on a single-ended clock, the noise will appear on the
reference plane and may be coupled to I/O traces. A differential clock's return path is the clock-bar
signal/trace, which is more isolated than the reference plane and minimizes potential I/O trace
coupling.
For best results, the trace lengths and routing of the clock lines must be closely matched, and
spacing between the two traces should be kept as small as possible. This will minimize loop area
and maximize H-field cancellation. In addition, the real and parasitic terminations of each signal of
a differential pair should be the same. Also, the skew between the signal level transitions on the
two lines must be small compared to the rise time of the level transitions.
Placing ground traces on the outside of the differential pair may further reduce emissions.
Intermediate vias to ground may be needed to reduce the opportunity for re-radiation from the
ground traces themselves. Distance between vias should be less than ¼ of a wavelength of the fifth
harmonic of the processor core frequency.
11.2.3
PCI Bus Clock Control
Experimental data has indicated a reduction in EMI may be possible by disabling the clocks to
unused (and therefore unterminated) PCI slots. CK408B, the clock chip that has been specified and
designed for this platform, supports individual control of the various PCI clocks. Designers have
the option to enable or disable individual PCI clocks depending upon their specific system
configuration requirements. Refer to the
CK408B Clock Synthesizer Design Guidelines
for details
on how to configure the PCI clocks.
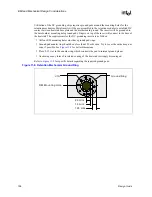
Figure 11-3. Cancellation of H-fields Through Inverse Currents
CLK - clock trace
CLK' - clock bar
trace
H-field
caused by
Iclk
Iclk
Iclk'
H-field
caused by
Iclk'
Summary of Contents for Xeon
Page 24: ...Introduction 24 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 30: ...Component Quadrant Layout 30 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 52: ...Platform Clock Routing Guidelines 52 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 66: ...System Bus Routing Guidelines 66 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 118: ...Intel 82870P2 P64H2 118 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 146: ...I O Controller Hub 146 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 148: ...Debug Port 148 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 210: ...Schematic Checklist 210 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 220: ...Layout Checklist 220 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 222: ...Schematics 222 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...