Design Guide
151
EMI and Mechanical Design Considerations
11.2.2
Differential Clocking
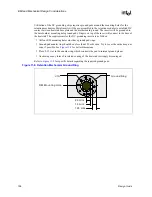
Differential clocking requires that the clock generator supply both clock and clock-bar traces.
Clock-bar has equal and opposite current as the primary clock, and is also 180 degrees out of
phase. To maximize the benefit of differential clocking, both clock lines must be routed parallel to
each other for their entire length. Devices connected to the clock must also be designed to accept
both the clock and clock-bar signals.
EMI reduction due to differential clocking is caused by H-field cancellation. Since H-field
orientation is generated by and is dependent upon current flow, two equal currents flowing in
opposite directions and 180 degrees out of phase will have their H-fields cancelled (see
). Lower H-fields will result in reduced EMI radiation.
Figure 11-1. Spread Spectrum Modulation Profile
Figure 11-2. Impact of Spread Spectrum Clocking on Radiated Emissions
(1-
δ
)f
nom
time
f
nom
1/f
m
∆
SCC
non-SSC
(1-
δ
)f
nom
f
nom
Summary of Contents for Xeon
Page 24: ...Introduction 24 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 30: ...Component Quadrant Layout 30 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 52: ...Platform Clock Routing Guidelines 52 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 66: ...System Bus Routing Guidelines 66 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 118: ...Intel 82870P2 P64H2 118 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 146: ...I O Controller Hub 146 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 148: ...Debug Port 148 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 210: ...Schematic Checklist 210 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 220: ...Layout Checklist 220 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 222: ...Schematics 222 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...