January 2007
215
Intel
®
855GME Chipset and Intel
®
6300ESB ICH Embedded Platform Design Guide
Intel
®
6300ESB Design Guidelines
9.6.4.1
Common-Mode Chokes
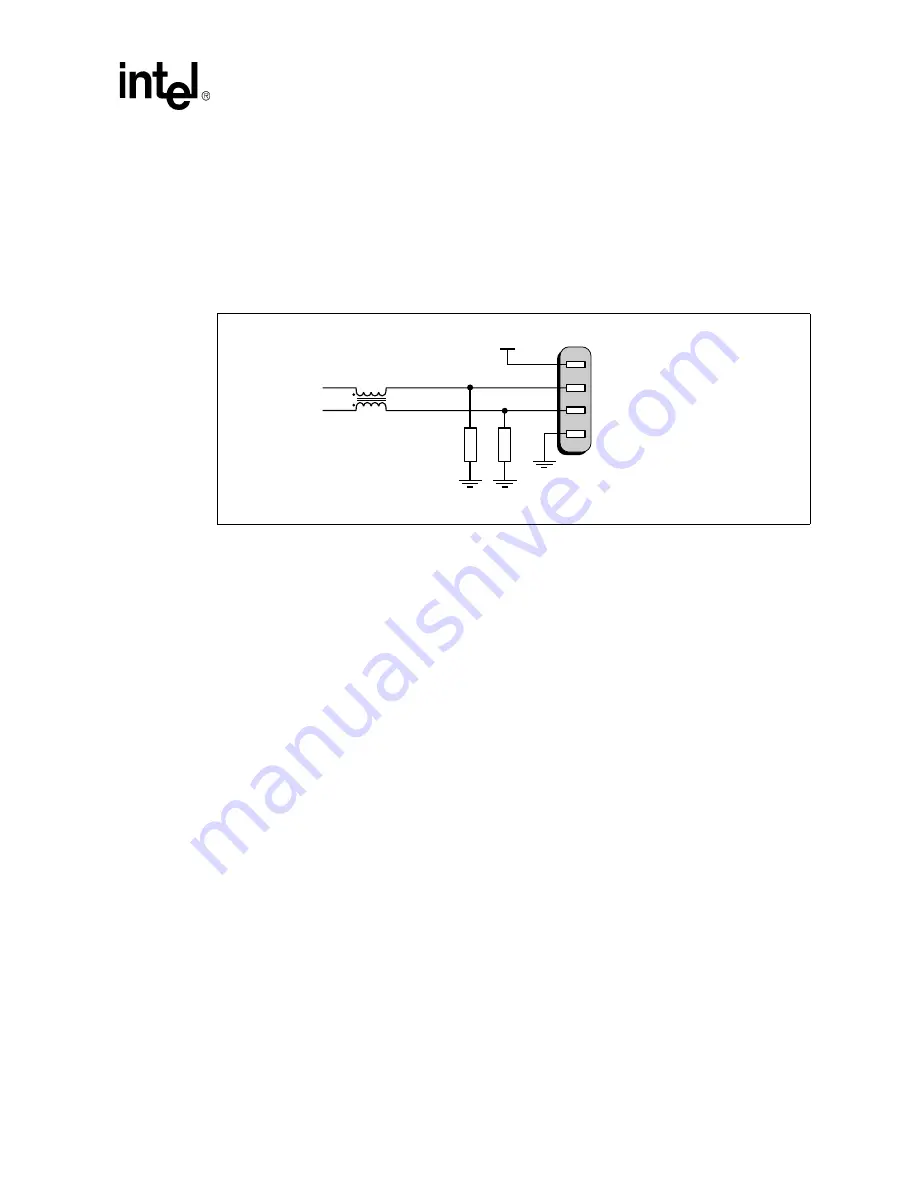
Testing has shown that common-mode chokes may provide required noise attenuation. A design
should include a common-mode choke footprint to provide a stuffing option in the event the choke
is needed to pass EMI testing.
shows the schematic of a typical common-mode choke
and ESD suppression components. Place the choke as close as possible to the USB connector
signal pins. In systems that route USB to a front panel header, place the choke on the front panel
card. (See
Section 9.6.6.3, “Front Panel Connector Card” on page 218
for more information.)
Common mode chokes distort full-speed and high-speed signal quality. As the common mode
impedance increases, the distortion will increase, so you should test the effects of the common
mode choke on full speed and high-speed signal quality. Common-mode chokes with a target
impedance of 80
Ω
to 100
Ω
at 100 MHz generally provide adequate noise attenuation.
Finding a common-mode choke that meets the designer’s needs is a two-step process.
1. A part must be chosen with the impedance value that provides the required noise attenuation.
This is a function of the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the part chosen and the
frequency and strength of the noise present on the USB traces that you are trying to suppress.
2. Once you have a part that gives passing EMI results the second step is to test the effect this
part has on signal quality. Higher impedance common-mode chokes generally have a greater
damaging effect on signal quality, so care must be used when increasing the impedance
without doing thorough testing. Thorough testing includes checking the signal quality for
low-speed, full-speed and high-speed USB operation.
9.6.5
ESD
Classic USB (1.0/1.1) provided ESD suppression using in line ferrites and capacitors that formed a
low pass filter. This technique doesn’t work for USB 2.0 due to the much higher signal rate of
high-speed data. ESD protection is needed for USB lines. Refer to the Intel® ICH Family USB
ESD Considerations Application Note for ESD protection implementation guidelines. A device
that has been tested successfully is based on spark gap technology. Proper placement of any ESD
protection device is on the data lines between the common-mode choke and the USB connector
data pins as shown in
. Other types of low-capacitance ESD protection devices may
work as well but were not investigated. As with the common mode choke solution, it is
recommended to include footprints for some type of ESD protection device as a stuffing option in
case it is needed to pass ESD testing.
Figure 111.
A Common-Mode Choke
B1163-01
V
CC
Common Mode
Choke
D–
ESD Suppression
Components
USB A
Connector
D+
Summary of Contents for 6300ESB ICH
Page 24: ...24 Intel 855GME Chipset and Intel 6300ESB ICH Embedded Platform Design Guide Introduction...
Page 102: ...102 Intel 855GME Chipset and Intel 6300ESB ICH Embedded Platform Design Guide...
Page 122: ...122 Intel 855GME Chipset and Intel 6300ESB ICH Embedded Platform Design Guide...
Page 190: ...190 Intel 855GME Chipset and Intel 6300ESB ICH Embedded Platform Design Guide Hub Interface...
Page 318: ...318 Intel 855GME Chipset and Intel 6300ESB ICH Embedded Platform Design Guide Layout Checklist...
















































