2 Installation
- 22 -
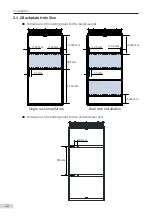
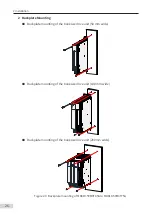
2.1.2 Backplate Hole Size
■
Dimensions of mounting holes for the booksize unit
≥
35
mm
≥
35
mm
≥
300
mm
≥
300
mm
50 mm
384
mm
≥
35
mm
≥
35
mm
≥
300
mm
≥
300
mm
50 mm
Single rack installation
Dual rack installation
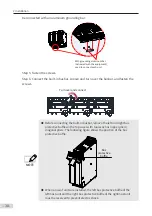
■
Dimensions of mounting holes for the vertical tower unit
105 mm
795
mm