3
6
SNMP Management
SNMP management and
iConfig
are always through the Uplink port of
Access
EtherLinX/4
. This provides a higher level of security because end-users cannot
access management, alter settings, etc.
Bandwidth Control
Access EtherLinX/4
includes bandwidth control functionality. Please refer to the
help file for software configuration information
Assigning IP Information
In order for
Access EtherLinX/4
to allow for SNMP-management, the unit must
be assigned IP configuration information (e.g., IP address, subnet mask, etc.) using
iConfig
via
iView²
;
the
unit’s serial port or DHCP
(
Dynamic Host Control
Protocol
). In addition to assigning an IP address and subnet mask, the former two
methods will also allow you to create community strings, assign access rights, con-
figure traps and more. However,
iConfig
offers more options than serial port con-
figuration (e.g., you can select
which
traps to assign with
iConfig
). After assigning
Access EtherLinX/4
an IP address, you can use
iView²
or another SNMP-compatible
Network Management System (NMS) to remotely configure, monitor and manage
Access EtherLinX/4.
A
B O U T
S
E R I A L
P
O R T
C
O N F I G U R A T I O N
Although
Access EtherLinX/4
does not include a DB-9 serial port, you can use
the supplied RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter on Downlink Port 4 to allow for serial port con-
figuration. This adapter uses an IBM-compatible DB-9 serial connector.
To connect
Access EtherLinX/4
to your terminal/computer, use a straight-through
(pin-to-pin) cable. (If your computer/terminal has a COM port using a connection
not compatible with a DB-9 connector, use the pin connection chart [below] for
reference in making a cable.) Make sure the cable length is under 50 ft. (15.24 m).
Plug one end of the cable into the DB-9 connector on
Access EtherLinX/4
and the
other into the appropriate port on your computer/terminal. Set your computer/ter-
minal for VT-100 emulation. The serial port on the computer/terminal should be
set for:
38.4K baud
,
8 data bits
,
1 stop bit
,
no parity
and
no flow control
.
Main Configuration Screen
After running through an initial self test, the screen will display the follow-
ing message: “
Press <Enter> for Device Configuration.
” Press
Enter
to be
taken to the main configuration screen. Here you will find several displays:
S
E R I A L
A
D A P T E R
P
I N
C
O N N E C T I O N
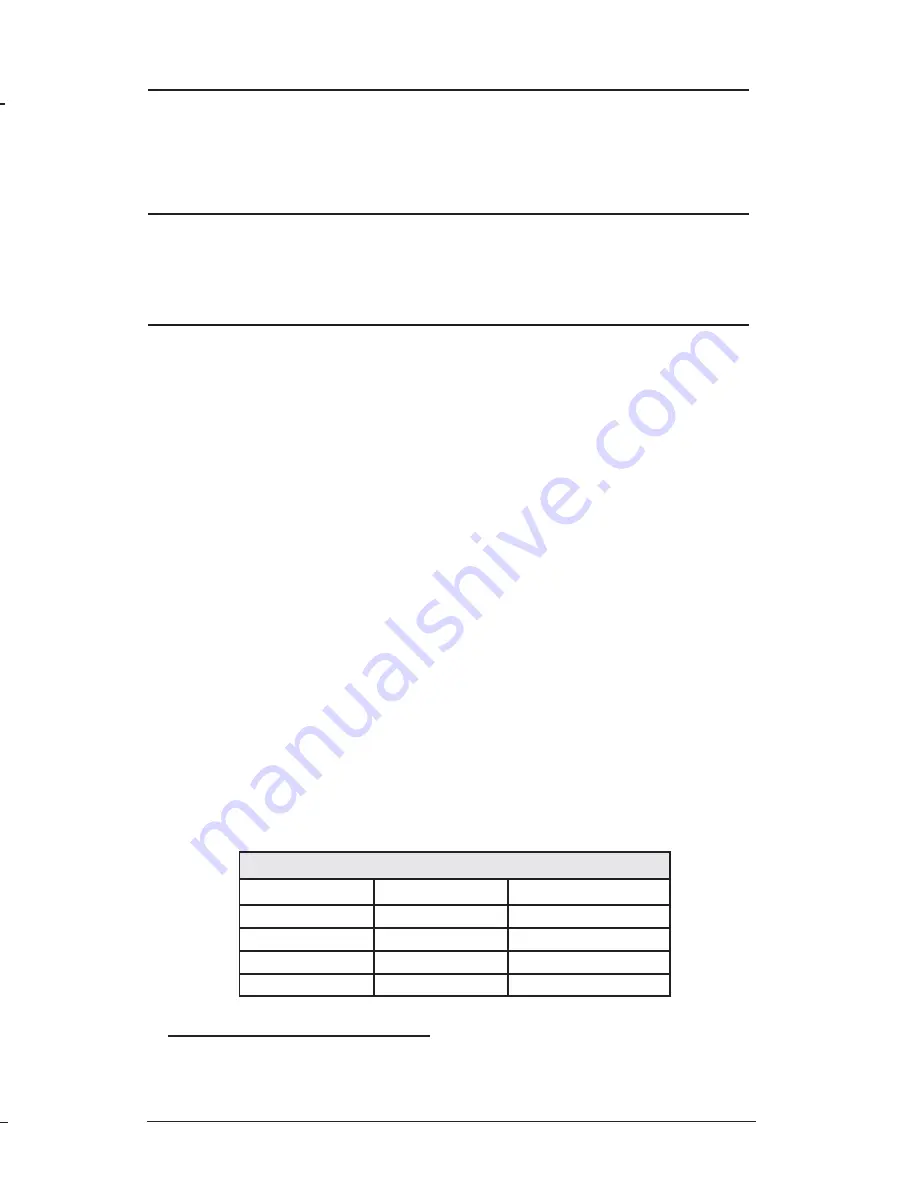
RJ-45 Pin #
DB-9 Pin #
Function
5
2
Transmit (OUT)
7
3
Receive (IN)
8
5
Ground
1
-4, 6
1
,
4, 6 - 9
Reserved
Device-Specific Configuration
C
O N F I G U R I N G
V L A N I D
S
LANs consist of devices that are grouped within a certain physical proximity.
Virtual LANs (VLANs) allow devices that are in different LANs to communicate
with each other as if they were part of the same LAN.
Access EtherLinX/4
is VLAN
compatible; it has the ability to accept traffic containing 802.1q VLAN tags on the
Uplink port and direct that traffic to the twisted pair downlink ports or to manage-
ment basedon VLAN ID.
To configure VLAN IDs, press the Space Bar when in the Command List section
of the Main Configuration screen (serial configuration). VLAN is an available
option. Type
VLAN
and press
Enter
to be taken to the
VLAN Configuration
screen.
To enable VLAN functionality, type
Y
(Yes) under Tags for the Uplink port, then
assign a separate VLAN ID for the Uplink port, each of the twisted pair downlink
ports and for management. Valid VLAN IDs are 1 to 4,094. Only the Uplink can
be enabled to forward tagged traffic.
To disable VLAN functionality, type
N
(No) under Tags for the Uplink port.
B
A S E
V L A N P
R I O R I T Y
The Uplink port has two outgoing queues; one for high priority traffic and one
for low priority traffic. Via
iView²
, you can set a Base VLAN Priority to designate
what will be high priority and low priority. If the Base VLAN Priority is 4, 0-3 are
low priority and 4-7 are high priority. If you change the Base VLAN Priority to 3,
0-2 are low priority and 3-7are high priority. In the
VLAN Configuration
screen
(shown above), enter a Priority (0 - 7) for each port and SNMP, if desired.









