5
2
the control plug of the clamp should be placed in the socket (6), and the gas connector plug in the socket of the
quick coupler (7). The gas pipe from the regulator should be connected and secured to the gas connector (16)
located on the back of the housing. Connect the positive pole of the source (5) with the workpiece using a cable
with a clamp. Connect the device's plug to a 230V 50Hz power socket.
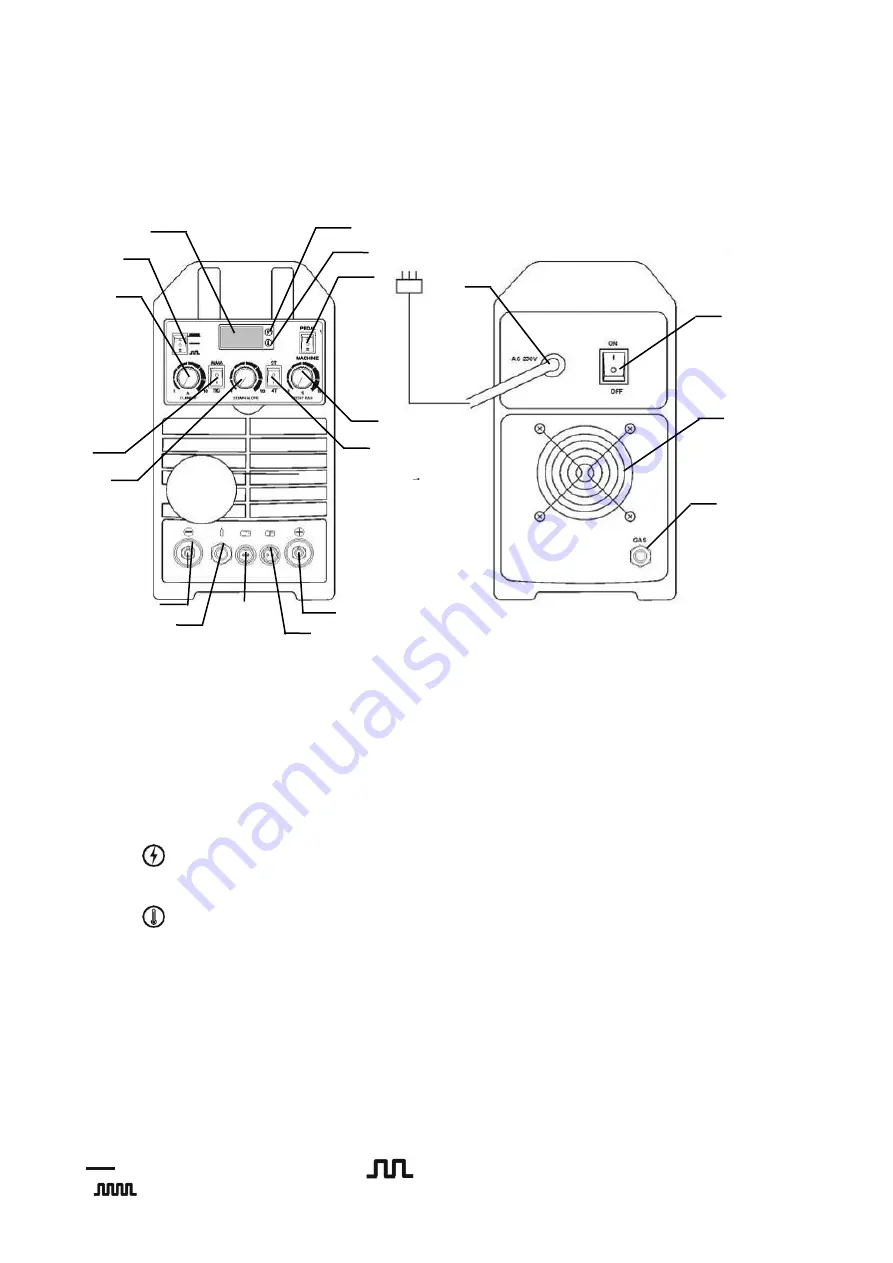
6 DESCRIPTION OF SWITCH FUNCTIONS AND KNOBS
6.1
Front and rear panel
1).Power supply LED
2).Thermal protection diode
3).Remote foot pedal and machine switch
4).Post gas adjustment knob
5).Control mode switch (two-stroke / four-stroke)
6).Display
7).Pulse frequency switch
8).Welding current adjustment knob
9).MMA/TIG switch
10).Down slope adjustment knob
11).Negative polarization socket
12).Shielding gas connection
13).Remote socket
14).Control socket
15).Positive polarity socket Fan
16).Power cord
17).Power on/off
18). Fan
19).Shielding gas cap
6.2 Control panel
Diode
The LED lights up when the device is turned on.
Diode
Overheat protection - the power source is equipped with a thermal automatic overload switch. When the
welder's temperature is too high, the protection disconnects the welding current and the LED lights up. After
the temperature drops, the circuit breaker will reset automatically.
Display of welding parameters
The display shows the welding current in amperes.
Welding method selection switch
The switch is used to select the welding method.
MMA
- welding with covered electrode (MMA),
TIG
-
welding with tungsten electrode in shielding gases.
Pulse frequency switch
Switch active only during TIG welding. Used to control the operation of the pulse:
pulseless welding
pulse frequency welding 1.2 Hz
pulse frequency welding 200 Hz
11
1
4
5
6
7
9
10
16
17
18
19
12 13
14
15
2
3
8


























