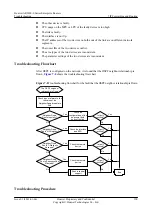
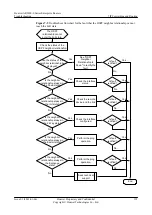
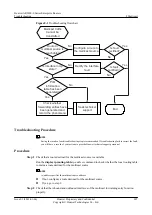
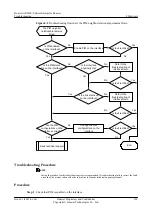
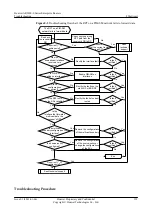
l
Results of the preceding troubleshooting procedure
l
Configuration files, log files, and alarm files of the devices
----End
Relevant Alarms and Logs
Relevant Alarms
OSPF_1.3.6.1.2.1.14.16.2.2 ospfNbrStateChange
OSPF_1.3.6.1.2.1.14.16.2.8 ospfIfRxBadPacket
OSPF_1.3.6.1.2.1.14.16.2.16 ospfIfStateChange
Relevant Logs
None.
7.4.3 Trouble Cases
Routes Are Abnormal Because the FA Fields in Type 5 LSAs Are Set Incorrectly
Fault Symptom
On the network shown in
, Router C is a non-Huawei device. Router A and
Router B are two routers. Router A and Router B have two upstream GE interfaces and are
configured with two static routes.
l
Router A
[RouterA]
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.69
[RouterA]
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.65
l
Router B
[RouterB]
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.5
[RouterB]
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1
Router A and Router B advertise default routes to Router C in an unforced manner. Normally,
Router C has a default external route to Router A and another default external route to Router
B. Router C, however, has a route to only one of Routers A and B in the following situations:
l
The static route 192.168.0.65 on Router A is deleted, and other configurations remain
unchanged. In this case, Router C has an OSPF default route to only Router B.
l
The static route 192.168.0.1 on Router B is deleted, and other configurations remain
unchanged. In this case, Router C has an OSPF default route to only Router A.
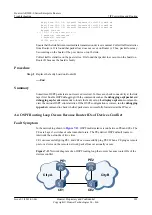
Figure 7-10
Network diagram of the networking where routes on a device are abnormal
192.168.1.253
RouterB
RouterA
GE1/0/0
192.168.1.254
GE2/0/0 GE1/0/0
GE2/0/0
RouterC
Huawei AR2200-S Series Enterprise Routers
Troubleshooting
7 IP Forwarding and Routing
Issue 01 (2012-01-06)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
198