Striping methods
There are two methods for configuring the physical layout of the disk arrays:
•
Vertical striping
•
Horizontal striping
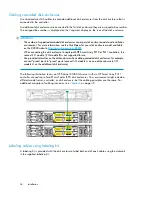
In a vertical configuration, a single RAID array uses one physical drive from each disk enclosure.
In a horizontal configuration, the RAID array uses multiple drives contained within one or more disk
enclosures.
RAID levels
Smart Array controllers use hardware-based RAID technology to group multiple disk drives together
in larger logical units (LUNs).
Key RAID methods include the use of data striping, data mirroring, and parity error checking. Data
striping improves speed by performing virtual disk I/O with an entire group of physical disks at the
same time. Mirroring provides data redundancy by storing data and a copy of the data. Parity error
checking provides automatic detection and correction if corruption of a physical disk occurs.
Depending on the host environment, the following RAID levels are supported with this disk enclosure:
RAID0, RAID1, RAID5 and RAID6 with ADG. Each level uses a different combination of RAID methods
that impact data redundancy, the amount of physical disk space used, and I/O speed. After you
create a LUN, you cannot change the RAID level.
The following table compares the different RAID levels.
RAID meth-
od
Data redund-
ancy
Best practices
Summary
Striping
None
IMPORTANT
: Do not use RAID0
for LUNs if fault tolerance is re-
quired. Consider RAID0 only for
noncritical storage. RAID0 LUNs
provide the best performance for
applications that use random I/O.
RAID0 is optimized for I/O
speed and efficient use of
physical disk capacity, but
provides no data redund-
ancy.
RAID0
Mirroring
High
In general, RAID1 virtual disks
provide better performance char-
acteristics over a wider range of
application workloads than
RAID5.
RAID1 is optimized for data
redundancy and I/O speed,
but uses the most physical
disk space.
IMPORTANT
:
RAID1 uses about 100%
more physical disk space
than RAID0 and 70% more
than RAID5.
RAID1
Striping and
parity
Medium
RAID5 virtual disks can provide
performance advantages over
RAID1 for some applications that
use sequential I/O. Consider
RAID5 disks for applications with
high sequential I/O of records in
multiples of 8K bytes. The larger
the record size, the greater the
advantage.
RAID5 provides a balance
of data redundancy, I/O
speed and efficient use of
physical disk space.
RAID5
D2600/D2700 Disk Enclosure User Guide
27
Summary of Contents for StorageWorks D2700
Page 10: ...Hardware 10 ...
Page 22: ...Technical specifications 22 ...
Page 32: ...Installation 32 ...
Page 68: ...Support and other resources 68 ...
Page 72: ...Bulgarian notice Czech notice Danish notice Dutch notice Regulatory compliance notices 72 ...
Page 74: ...Greek notice Hungarian notice Italian notice Latvian notice Regulatory compliance notices 74 ...
Page 80: ...80 ...