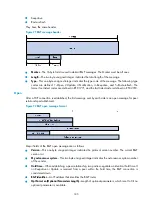
174
Number of LSPs Awaited: 3
T3 Timer Status:
Remaining Time: 140
T2 Timer Status:
Remaining Time: 59
IS-IS(1) Level-2 Restart Status
Restart Interval: 150
SA Bit Supported
Total Number of Interfaces = 1
Restart Status: RESTARTING
Number of LSPs Awaited: 3
T3 Timer Status:
Remaining Time: 140
T2 Timer Status:
Remaining Time: 59
IS-IS NSR configuration example
Network requirements
Switch S, Switch A, and Switch B belong to the same IS-IS routing domain as illustrated in
Switch S is an IRF fabric, which is connected to Switch A and Switch B over aggregated links. Enable IS-IS
NSR on Switch S to ensure correct routing when a master/slave switchover occurs on Switch S.
Figure 67
Network diagram for IS-IS NSR configuration
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure IP addresses and subnet masks for interfaces on the switches. (Details not shown.)
2.
Configure IS-IS on the switches, ensuring that Switch S, Switch A, and Switch B can communicate
with each other at Layer 3 and dynamic route update can be implemented among them with IS-IS.
(Details not shown.)
3.
Enable IS-IS NSR on Switch S.
<SwitchS> system-view
[SwitchS] isis 1
[SwitchS-isis-1] non-stop-routing
[SwitchS-isis-1] non-stop-routing interval 30
[SwitchS-isis-1] return
4.
Verify the configuration:
After Switch S establishes neighbor relationships with Switch A and Switch B, they start to
exchange routing information. After network convergence, perform a master/slave switchover on
Switch S. During the switchover period, use the
display isis peer
command to check the neighbor
relationship between Switch A and Switch S and between Switch B and Switch S; use the
display