235
Configuring QoS
The Web interface provides the following QoS configuration functions:
•
Configuring subnet limit
•
Configuring advanced limit
•
Configuring advanced queue
Overview
Quality of Service (QoS) is a concept concerning service demand and supply. It reflects the ability to
meet customer needs. Generally, QoS focuses on improving services under certain conditions rather than
grading services precisely.
In an Internet, QoS evaluates the ability of the network to forward packets of different services. You can
base the evaluation on different criteria because the network provides various services. Generally, QoS
refers to the ability to provide improved service by solving the core issues such as delay, jitter, and packet
loss ratio in the packet forwarding process.
Through the Web interface, you can configure the following QoS features:
•
•
•
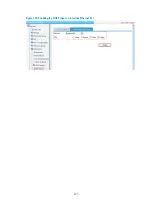
Subnet limit
Subnet limit enables you to regulate the specification of traffic entering or leaving a device based on
source/destination IP address. Packets conforming to the specification can pass through, and packets
exceeding the specification are dropped. In this way, the network resources are protected.
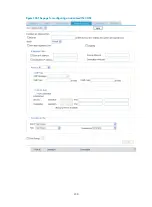
Advanced limit
Similar to subnet limit, advanced limit also implements traffic policing at the IP layer. They differ in that:
•
Advanced limit can classify traffic based on time range, packet precedence, protocol type, and
port number, and provide more granular services.
•
In addition to permitting traffic conforming to the specification to pass through, advanced limit can
also set IP precedence, differentiated service code point (DSCP) value, and 802.1p priority for
packets as required.
For more information about IP precedence, DSCP values, and 802.1p priority, see "
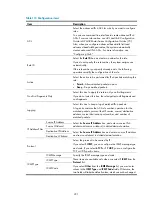
Advanced queue
Advanced queue offers the following functions:
•
Interface bandwidth limit
—Uses token buckets for traffic control and limits the rate of transmitting
packets (including critical packets) on an interface. When limiting the rate of all packets on an
Summary of Contents for MSR SERIES
Page 17: ...xv Documents 835 Websites 835 Conventions 836 Index 838 ...
Page 20: ...3 Figure 3 Initial page of the Web interface ...
Page 42: ...25 Figure 13 Firefox Web browser setting ...
Page 59: ...42 Figure 27 Checking the basic service configuration ...
Page 73: ...56 Figure 35 Sample interface statistics ...
Page 156: ...139 Figure 139 Rebooting the 3G modem ...
Page 168: ...151 Figure 152 Configuring Web server 2 ...
Page 174: ...157 Figure 158 Configure the URL filtering function ...
Page 242: ...225 Figure 233 Enabling the DHCP client on interface Ethernet 0 1 ...
Page 247: ...230 Figure 236 The page for configuring an advanced IPv4 ACL ...
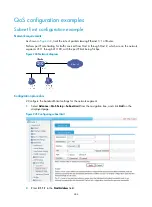
Page 255: ...238 Figure 241 Advanced limit setting ...
Page 298: ...281 e Click Apply 2 Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured ...
Page 400: ...383 Figure 387 Verifying the configuration ...
Page 405: ...388 ...
Page 523: ...506 Figure 530 Ping configuration page ...
Page 775: ...758 Figure 785 Configuring a jump node ...