312
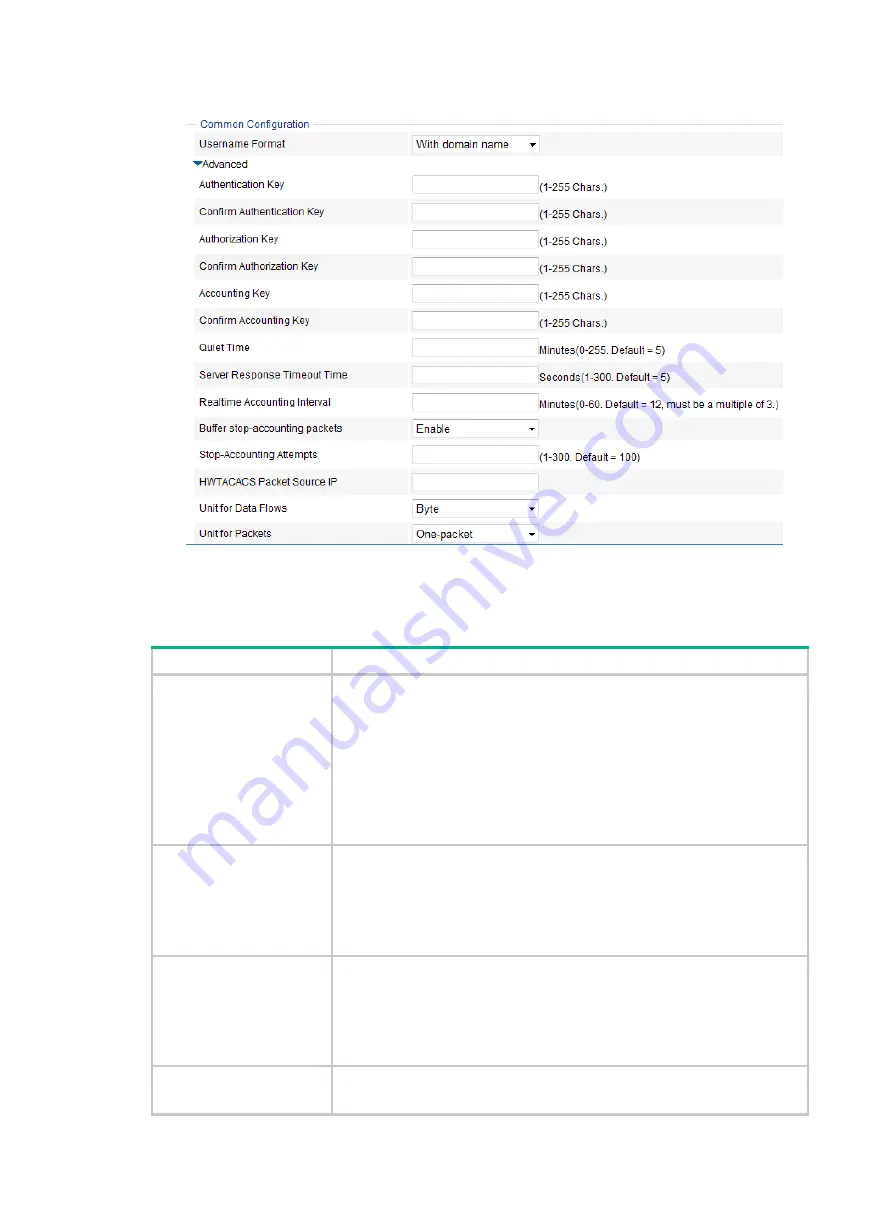
Figure 333 HWTACACS communication parameter configuration
3.
Configure the HWTACACS parameters as described in
4.
Click
Apply
.
Table 112 Configuration items
Item Description
Username Format
Set the format of the usernames sent to the HWTACACS servers.
A username is typically in the
userid
@
isp-name
format, of which the
isp-name
argument is used by the device to determine the ISP domain to which the user
belongs. If HWTACACS servers cannot recognize usernames that contain
ISP domain names, you can configure the device to send usernames without
domain names to the servers.
Options include:
•
Without domain name
—Excludes the domain name from a username.
•
With domain name
—Includes the domain name in a username.
Authentication Key
Confirm Authentication Key
Enter the authentication shared key and confirm the key.
The HWTACACS client (the HPE NJ5000 5G PoE+ switch) and HWTACACS
authentication server use the MD5 algorithm to encrypt packets exchanged
between them and use a shared key to verify the packets. Make sure the
HWTACACS server and client use the same shared key for secure
communication.
Authorization Key
Confirm Authorization Key
Enter the authorization shared key and confirm the key.
The HWTACACS client (the HPE NJ5000 5G PoE+ switch) and HWTACACS
authorization server use the MD5 algorithm to encrypt packets exchanged
between them and use a shared key to verify the packets. Make sure the
HWTACACS server and client use the same shared key for secure
communication.
Accounting Key
Confirm Accounting Key
Enter the accounting shared key and confirm the key.
The HWTACACS client (the HPE NJ5000 5G PoE+ switch) and HWTACACS
Summary of Contents for FlexNetwork NJ5000
Page 12: ...x Index 440 ...
Page 39: ...27 Figure 16 Configuration complete ...
Page 67: ...55 Figure 47 Displaying the speed settings of ports ...
Page 78: ...66 Figure 59 Loopback test result ...
Page 158: ...146 Figure 156 Creating a static MAC address entry ...
Page 183: ...171 Figure 171 Configuring MSTP globally on Switch D ...
Page 243: ...231 Figure 237 IPv6 active route table ...






























