230
Task Command
Display the contents of a certificate.
display pki certificate
domain
domain-name
{
ca
|
local
|
peer
[
serial
serial-num
]
}
Display certificate request status.
display pki certificate request-status
[
domain
domain-name
]
Display locally stored CRLs in a PKI
domain.
display pki crl domain
domain-name
Display certificate attribute group
information.
display pki certificate attribute-group
[
group-name
]
Display certificate-based access control
policy information.
display pki certificate access-control-policy
[
policy-name
]
PKI configuration examples
You can use different software applications, such as Windows server, RSA Keon, and OpenCA, to act as
the CA server.
If you use Windows server or OpenCA, you must install the SCEP add-on for Windows server or enable
SCEP for OpenCA. In either case, when you configure a PKI domain, you must use the
certificate request
from ra
command to specify the RA to accept certificate requests.
If you use RSA Keon, the SCEP add-on is not required. When you configure a PKI domain, you must use
the
certificate request from ca
command to specify the CA to accept certificate requests.
Requesting a certificate from an RSA Keon CA server
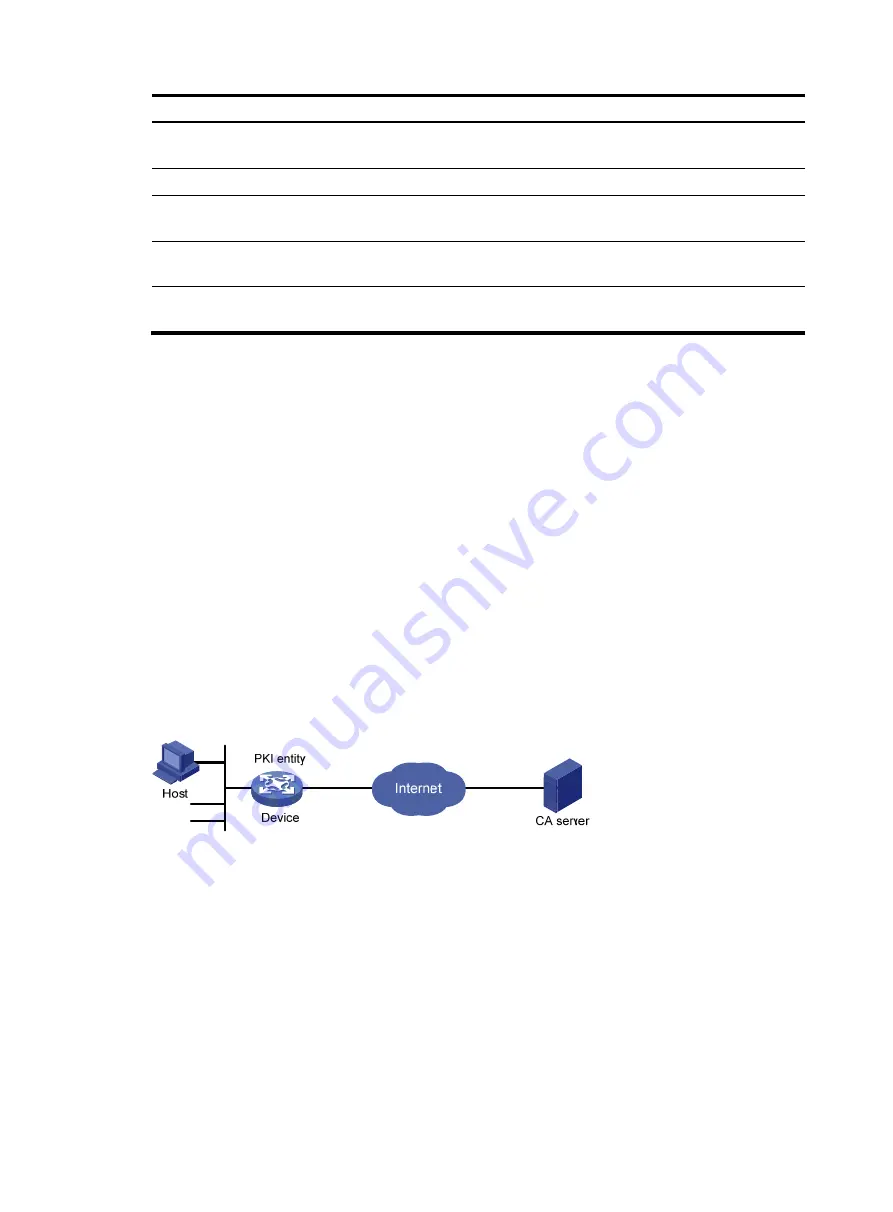
Network requirements
Configure the PKI entity (the device) to request a local certificate from the CA server.
Figure 74
Network diagram
Configuring the RSA Keon CA server
1.
Create a CA server named
myca
:
In this example, you must configure these basic attributes on the CA server:
{
Nickname
—Name of the trusted CA.
{
Subject DN
—DN attributes of the CA, including the common name (CN), organization unit
(OU), organization (O), and country (C).
You can use the default values for other attributes.
2.
Configure extended attributes:
Configure parameters in the
Jurisdiction Configuration
section on the management page of the CA
server:
















































