36
Configuring bidirectional control detection
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter RIP view.
rip
[
process-id
] [
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name
]
N/A
3.
Specify a RIP neighbor.
peer
ip-address
By default, RIP does not unicast
updates to any peer.
Because the
undo peer
command
does not remove the neighbor
relationship immediately,
executing the command cannot
bring down the BFD session
immediately.
4.
Enter interface view.
interface
interface-type
interface-number
N/A
5.
Enable BFD on the RIP
interface.
rip bfd enable
By default, BFD is disabled on a RIP
interface.
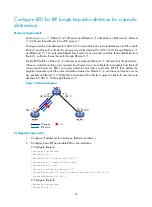
Configuring RIP FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop until RIP completes routing
convergence based on the new network topology. FRR enables fast rerouting to minimize the impact of
link or node failures.
Figure 6
Network diagram for RIP FRR
, configure FRR on Router B by using a routing policy to specify a backup next hop. When the
primary link fails, RIP directs packets to the backup next hop. At the same time, RIP calculates the shortest
path based on the new network topology, and forwards packets over that path after network
convergence.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
•
RIP FRR takes effect only for RIP routes learned from directly connected neighbors.
•
Do not use RIP FRR and BFD for RIP at the same time. Otherwise, FRR might fail to work.
•
RIP FRR is available only when the state of primary link (with Layer 3 interfaces staying up) changes
from bidirectional to unidirectional or down.