291
Destination: 1200::/64
Protocol: BGP4+ Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h00m57s
Cost: 100 Preference: 255
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x1 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0xa OrigAs: 0
NBRID: 0x25000000 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0x0 Neighbor: 2001::1
Flags: 0x10060 OrigNextHop: 2001::1
Label: NULL RealNextHop: FE80::20C:29FF:FE40:715
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: N/A
Tunnel ID: Invalid Interface: Ethernet1/2
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkInterface: N/A
The output shows that Router C communicates with network 1200::0/64 through the path Router
C<—>Router D<—>Router A.
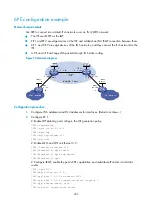
IPsec for IPv6 BGP packets configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in
, all routers run IPv6 BGP. Establish an IBGP connection between Router A and
Router B. Establish an EBGP connection between Router B and Router C.
To enhance security, configure IPsec to protect IPv6 BGP packets.
Figure 76
Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure IPv6 addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2.
Establish an IBGP connection between Router A and Router B:
# Configure Router A.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] bgp 65008
[RouterA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1
[RouterA-bgp] group ibgp internal
[RouterA-bgp] peer 1::2 group ibgp
[RouterA-bgp] address-family ipv6 unicast
[RouterA-bgp-ipv6] peer ibgp enable
[RouterA-bgp-ipv6] quit
[RouterA-bgp] quit
# Configure Router B.
<RouterB> system-view