6
© 2022 S. Himmelstein and Company—all rights reserved. www.himmelstein.com
B. Electrical Installation
B.1 Applicability
This section applies to all MCRT
®
48200V Torquemeters.
B.2 Stator Connectors
Three stator connectors are used, as follows:
• Input Power (2 Pins)
• Analog Output/Cal Enable/Zero (4 Pins)
• Com Port (3 Pins)
If an optional speed pickup is furnished, it will have an
integral 2 pin (Code A) or 3 pin (Code Z) connector.
The
Code Z Zero Velocity Pickup is recommended for use
at low operating speed and for electrically noisy envi-
ronments.
Mating connectors are supplied except if a
complete cable is furnished for the Com Port.
Before wiring mating connectors, refer to Figure 5 for the
connector pin number identification(s). That Figure shows
the stator connector looking down at the torquemeter.
Mating connector pin sequence is their mirror image.
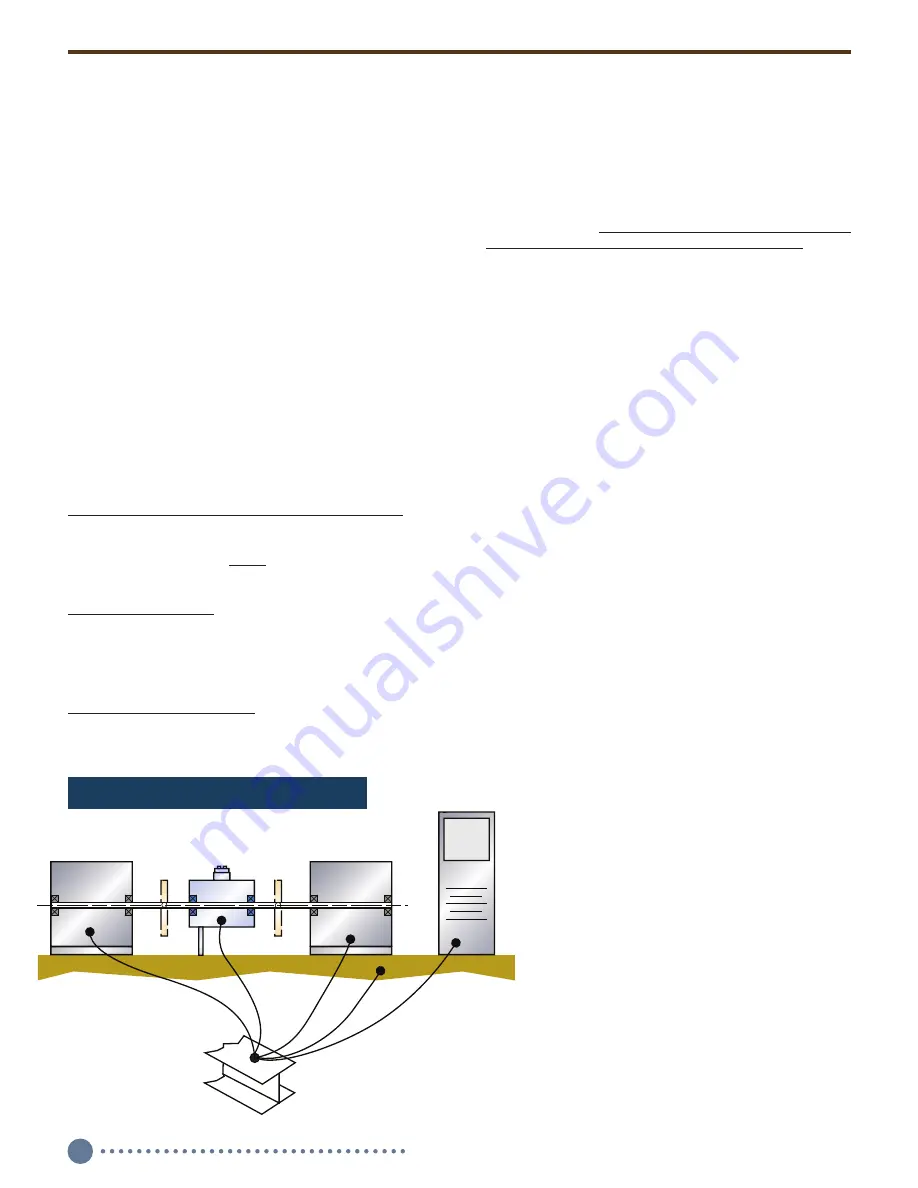
B.2.1 Earth Ground Connection
Connect the Torquemeter stator directly to earth ground, a
buildings’ structural steel or a floor rod. If neither is avail-
able, drive a six foot copper rod into the floor. Then run
separate ground straps between it, the drive motor frame,
the machine base, the torquemeter housing, the load
device and the data acquisition/computer system ground.
Don’t “daisy chain” the connections. See Figures 3 and 4.
If an IGBT-based variable frequency drive (VFD) is used,
follow its installation manual. Improperly installed VFD’s
can cause premature motor and cable failures, and
reading errors from excessive noise. VFD’s should have
shielded power and motor cables. Belden Types 29500
thru 29507 cable are designed for VFD use. See “Cable
Alternatives for PWM AC Drive Applications” available at
www.belden.com. Himmelstein recommends the connec-
tion in
Figure 20
. For best results, use a differential input
amplifier in these electrically noisy environments.
B.2.2 Power Input; 2 Pin Connector
The power connector has two pins with pinout as follows:
Pin 1
Power Return
Pin 2
+ Power In ( 10 to 15 VDC)
Spare mating connectors can be ordered from the factory;
P/N: 320-1285.
Reverse polarity protection is standard. Although any wire
may be used for connections,
shielded cable will perform
best in noisy environments and is recommended
. Note:
the shield should float at the Torquemeter end. The other
end should be tied to earth ground; see Figure 5.
Caution: Don’t connect a Torquemeter to a
Power Supply that also drives inductors or
solenoids. Induced switching transients may
cause damage or noise.
B.2.3 Analog Outputs, Cal Enable, Torque
Zeroing; 4 Pin Connector
Shielded cable is recommended for these connections.
The shield should float at the Torquemeter end and tied
to earth ground at the other end; See Figure 5. Spare
mating connectors can be ordered from the factory; P/N:
320-1287.
B.2.3.1 Analog Outputs
An analog of Torque is output on the four pin connector.
Pin connections are as follows:
Pin 1
Analog Output
Pin 2
Analog Ground
The analog signal may have full scale values as
follows:
Torque CW = +10V, CCW = -10V, or
CW = +5V, CCW = -5V
The default value is 10 Volts. The user may reas-
sign the output voltage selection with the use of
a PC and supplied software. CW torque causes
the shaft to turn CW when viewed from the
driven end. CCW torque causes the opposite
rotation.
B.2.3.2 Cal Check Enable
Internal Calibration Check Circuitry may be
remotely enabled by pin strapping and/or via
Load Device
DAS/Controller
Machine Base
Drive Motor
Torquemeter
Earth Ground
NOTE: Use separate
ground straps.
Figure 3. Correct System Earth Grounding.




















