APEX
™
Exciter Incorporating FLO
™
Technology
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Exciter Troubleshooting Flow Charts
Page: 5-14
888-2604-001
03/08/07
WARNING: Disconnect primary power prior to servicing.
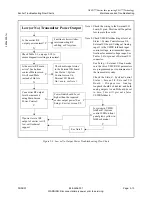
Figure 5-7 Transmitter Fails Mask Test Troubleshooting Flow Chart
Transmitter Fails Mask Test
N
Y
N
Y
This mode must be active for exciter
to perform non-linear correction,
which effects mask performance, See
Note 1.
Note 3: Refer to the technical manuals
for your transmitter to determine exact
RF feedback connections. Chapter 2
shows typical RF feedback connec-
tions for various Harris transmitters.
Is transmitter PA RF sample connected to exciter? See
Note 3. Is this sample at the correct level, see Note 4. This
sample is necessary for exciter to perform non-linear
correction, which effects mask performance.
Is exciter RTAC Non-Lin
correction in Adapt
mode? See exciter Main
Screen.
Are the status screen
diagnostics function all
set to normal? SeeTable
5-1, on page 5-10
If one or more diagnostic functions are
active, normal operation of exciter may
be impaired.
At this point, obvious causes of problem
have been eliminated. Call Technical
Support.
Section 5.7.3, Checking
Transmitter Spectrum, on
page 5-18 can be used to
determine stage where
shoulder response has failed.
See Note 6.
Note 1: See RTAC in Section 3.2,
Starting Point: The Main LCD Touch
Screen, on page 3-2
Is transmitter operating at or
below its rated output
power, and is it correctly
calibrated?
N
Y
Check RF output power calibration of
transmitter. If RF system is overdriven,
its resultant non-linearity may be outside
of RTAC correction range
Is the Status > Adaptive
Processing screen normal?
See Figure 3-7, on page 3-9
N
Y
This screen shows the PA feedback
sample level, see Notes 2. Is this
feedback sample out of range or
Faulted?
Note 2: In Adaptive Processing status
screen, PA Feedback and ADT
Overrange functions should show OK.
The Yellow and Blue horizontal Bars
represent RF sample level. They
should fall within middle 2/3rds of box
if their levels are correct. Yellow =
average level and blue = peak level.
Refer to Section 3.4.3, Adaptive
Processing Board Status Screen, on
page 3-9 for additional information.
Note 4: The correct sample input
power range, measured at the at the
exciter rear panel sample input cable,
is -30 to 0 dBm.
Is transmitter’s RF PA system is faulty?
If so, resultant non-linearity may be
outside of RTAC correction range.
Y
Note 5: This problem could be caused
by the exciter Chart Source (RF
spectrum display) selection not being
set to Tx-Pre HPF or Tx Post HPF.
This screen is found under Setup >
Setup Screen > Display Setup. For
more information, see Section 3.6.4,
Display Setup Screen, on page 3-41.
If linearity still looks bad at transmitter
output but looks good on exciter screen,
see Note 5.
N
N
Y
Filter Type:
Use FLO BANDPASS
because of the application of this exciter.
Use
Standard
if the standard D-Mask filter is used.
Use Asymm
(asymmet-
rical) if the sharp tuned filter (sometimes called “Cool Fuel”) is used or if the
group delay for the transmitter is not symmetrical, such as when its output is
reflected through an adjacent channel sharp tuned filter in order to combine
the two transmitters.
Exciter must be restarted
to make filter change active.
In the Setup > RTAC Setup
screen, does the Filter Type
choice match the HPF in the
transmitter System?
Y
Note 6: Shoulders refers to the
spectral response just outside the
channel limits.