Operation
This metal detector distinguishes between ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous metals contain iron.
Non-ferrous metals do not (examples: gold, silver, copper, platinum, aluminum, lead, and zinc).
When the Metal Detector senses a metallic object, the meter reading changes and the detector might
sound a tone. The reaction depends on what metal is detected.
Turning On The Metal Detector:
1. Set the
BATT TEST
to
OPERATE.
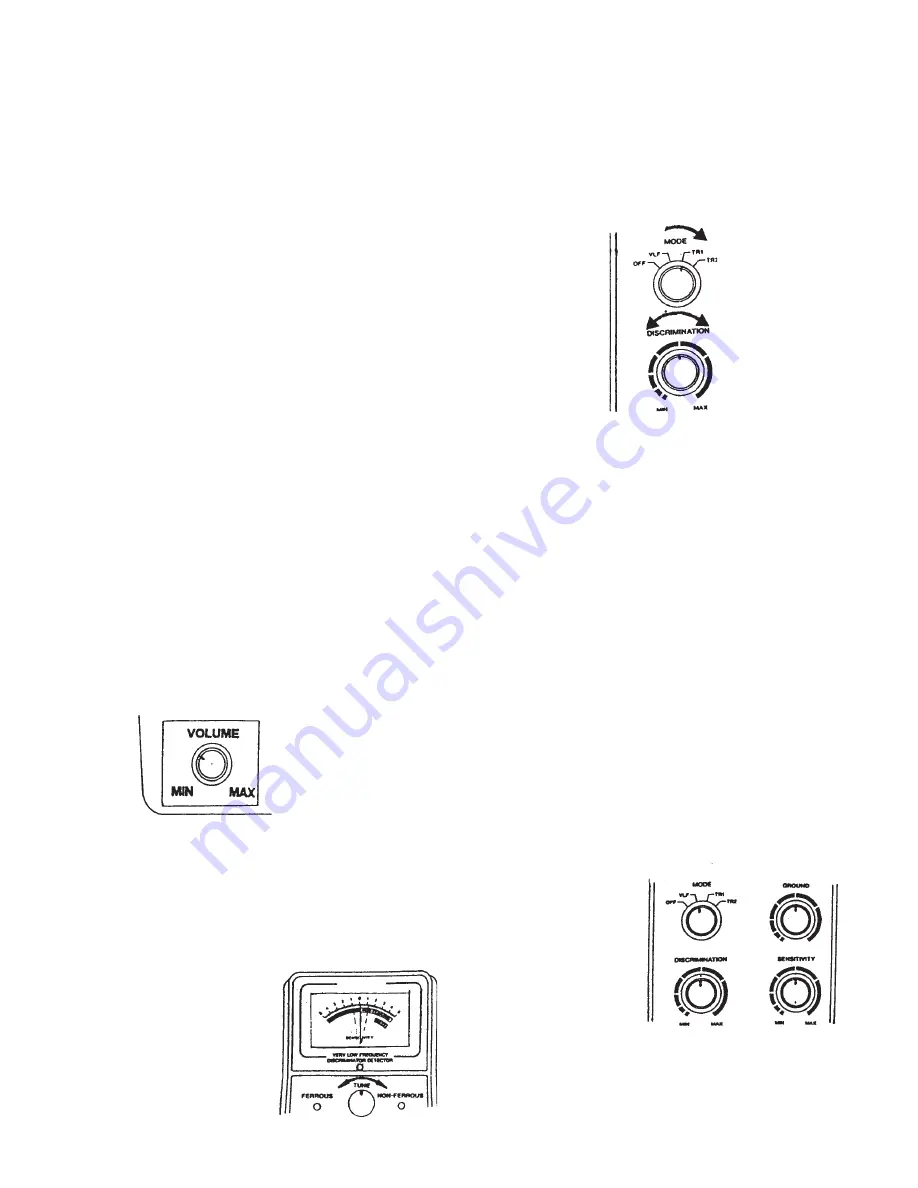
2. Hold the detector comfortably, then as shown in Figure 13,
rotate
MODE
to the desired position.
Set it to
VLF
to test the
battery power and adjust
TUNE
and
GROUND
(see directions below and on page 8 ).
Set it to
TR1
to detect extreme differences in metals, such
as between gold and iron. The difference shows on the meter (iron as a ferrous metal, gold as a
non-ferrous metal).
Set it to
TR2
to detect finer distincions between metals. For example, between aluminum and
gold.
Tuning the Metal Detector:
TUNE
fine tunes the balance between the metal detector’s receiver and the transmitter circuitry, to
provide consistent pointer and tone indications.
To set the
TUNE
, please do the following and see Figure 14 and 15:
1. Rotate
VOLUME
to the 10 o’clock position.
2. Set
MODE
to
VLF.
3. Set
GROUND
,
DISCRIMINATION
, and
SENSITIVITY
to mid-
range.
4. Hold the search coil at least 1 foot away from the ground and any
metal object. Hold down the red button on the handle and slowly
rotate
TUNE
until the viewmeter pointer rests at or near 0 (see Figure 16).
Figure 13
Figure 14
Figure 15
Figure 16
#43149 Page 6
Summary of Contents for 43149
Page 10: ... 43149 Page 10 ...
Page 11: ... 43149 Page 11 ...
Page 13: ... 43149 Page 13 ...
Page 14: ... 43149 Page 14 ...
Page 15: ... 43149 Page 15 ...
Page 17: ... 43149 Page 17 Wiring Diagram continued on next page ...
Page 18: ... 43149 Page 18 Wiring Diagram continued from prior page ...


















